Introduction to DIP
Signal processing is a discipline in electrical engineering and in mathematics that deals with analysis and processing of analog and digital signals , and deals with storing , filtering , and other operations on signals. These signals include transmission signals , sound or voice signals , image signals , and other signals etc.
Out of all these signals , the field that deals with the type of signals for which the input is an image and the output is also an image is done in image processing. As it name suggests, it deals with the processing on images.
It can be further divided into analog image processing and digital image processing.
Analog image processing
Analog image processing is done on analog signals. It includes processing on two dimensional analog signals. In this type of processing, the images are manipulated by electrical means by varying the electrical signal. The common example include is the television image.
Digital image processing has dominated over analog image processing with the passage of time due its wider range of applications.
Digital image processing
The digital image processing deals with developing a digital system that performs operations on an digital image.
What is an Image
An image is nothing more than a two dimensional signal. It is defined by the mathematical function f(x,y) where x and y are the two co-ordinates horizontally and vertically.
The value of f(x,y) at any point is gives the pixel value at that point of an image.
The above figure is an example of digital image that you are now viewing on your computer screen. But actually , this image is nothing but a two dimensional array of numbers ranging between 0 and 255.
128 30 123
232 123 321
123 77 89
80 255 255
Each number represents the value of the function f(x,y) at any point. In this case the value 128 ,
230 ,123 each represents an individual pixel value. The dimensions of the picture is actually the dimensions of this two dimensional array.
Relationship between a digital image and a signal
If the image is a two dimensional array then what does it have to do with a signal? In order to understand that , We need to first understand what is a signal?
Signal
In physical world, any quantity measurable through time over space or any higher dimension can be taken as a signal. A signal is a mathematical function, and it conveys some information.
A signal can be one dimensional or two dimensional or higher dimensional signal. One dimensional signal is a signal that is measured over time. The common example is a voice signal.
The two dimensional signals are those that are measured over some other physical quantities.
The example of two dimensional signal is a digital image. We will look in more detail in the
next tutorial of how a one dimensional or two dimensional signals and higher signals are formed and interpreted.
Relationship
Since anything that conveys information or broadcast a message in physical world between two observers is a signal. That includes speech or human voice human voice or an image as a signal. Since when we speak , our voice is converted to a sound wave/signal and transformed with respect to the time to person we are speaking to. Not only this , but the way a digital camera works, as while acquiring an image from a digital camera involves transfer of a signal from one part of the system to the other.
How a digital image is formed
Since capturing an image from a camera is a physical process. The sunlight is used as a source of energy. A sensor array is used for the acquisition of the image. So when the sunlight falls upon the object, then the amount of light reflected by that object is sensed by the sensors, and a continuous voltage signal is generated by the amount of sensed data. In order to create a digital image , we need to convert this data into a digital form. This involves sampling and quantization. The result of sampling and quantization results in an two dimensional array or matrix of numbers which are nothing but a digital image.
Overlapping fields
Machine/Computer vision
Machine vision or computer vision deals with developing a system in which the input is an image and the output is some information. For example: Developing a system that scans human face and opens any kind of lock. This system would look something like this.
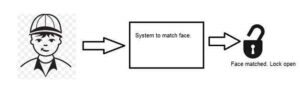
Computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with the formation of images from object models, rather then the image is captured by some device. For example: Object rendering. Generating an image from an object model. Such a system would look something like this.
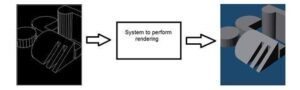
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is more or less the study of putting human intelligence into machines. Artificial intelligence has many applications in image processing. For example: developing computer aided diagnosis systems that help doctors in interpreting images of X-ray , MRI etc and then highlighting conspicuous section to be examined by the doctor.
Signals
In electrical engineering, the fundamental quantity of representing some information is called a signal. It does not matter what the information is i-e: Analog or digital information. In mathematics, a signal is a function that conveys some information. In fact any quantity measurable through time over space or any higher dimension can be taken as a signal. A signal could be of any dimension and could be of any form.
Analog signals
A signal could be an analog quantity that means it is defined with respect to the time. It is a continuous signal. These signals are defined over continuous independent variables. They are difficult to analyze, as they carry a huge number of values. They are very much accurate due to a large sample of values. In order to store these signals , you require an infinite memory because it can achieve infinite values on a real line. Analog signals are denoted by sin waves.
For example: Human voice
Human voice is an example of analog signals. When you speak, the voice that is produced travel through air in the form of pressure waves and thus belongs to a mathematical function, having independent variables of space and time and a value corresponding to air pressure. Another example is of sin wave which is shown in the figure below. Y = sinx where x is independent

Digital signals
As compared to analog signals, digital signals are very easy to analyze. They are discontinuous signals. They are the appropriation of analog signals.
The word digital stands for discrete values and hence it means that they use specific values to represent any information. In digital signal, only two values are used to represent something i-e: 1 and 0 binary values. Digital signals are less accurate then analog signals because they are the discrete samples of an analog signal taken over some period of time. However digital signals are not subject to noise. So they last long and are easy to interpret. Digital signals are denoted by square waves.
For example: Computer keyboard
Whenever a key is pressed from the keyboard, the appropriate electrical signal is sent to keyboard controller containing the ASCII value that particular key. For example the electrical signal that is generated when keyboard key a is pressed, carry information of digit 97 in the form of 0 and 1, which is the ASCII value of character a.
Difference between analog and digital signals
| Comparison element | Analog signal | Digital signal |
| Analysis | Difficult | Possible to analyze |
| Representation | Continuous | Discontinuous |
| Accuracy | More accurate | Less accurate |
| Storage | Infinite memory | Easily stored |
| Subject to Noise | Yes | No |
| Recording Technique | Original signal is preserved | Samples of the signal are taken and preserved |
Examples Human voice, Thermometer, Analog phones e.t.c Computers, Digital Phones, Digital pens, etc.
Systems
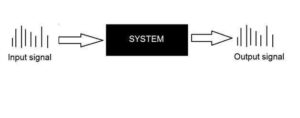
A system is a defined by the type of input and output it deals with. Since we are dealing with signals, so in our case, our system would be a mathematical model, a piece of code/software, or a physical device, or a black box whose input is a signal and it performs some processing on that signal, and the output is a signal. The input is known as excitation and the output is known as response.

In the above figure a system has been shown whose input and output both are signals but the input is an analog signal. And the output is an digital signal. It means our system is actually a conversion system that converts analog signals to digital signals.
Why do we need to convert an analog signal to digital signal.
The first and obvious reason is that digital image processing deals with digital images, that are digital signals. So when ever the image is captured, it is converted into digital format and then it is processed.
The second and important reason is, that in order to perform operations on an analog signal with a digital computer, you have to store that analog signal in the computer. And in order to store an analog signal, infinite memory is required to store it. And since thats not possible, so thats why we convert that signal into digital format and then store it in digital computer and then performs operations on it.
Continuous systems vs discrete systems Continuous systems
The type of systems whose input and output both are continuous signals or analog signals are called continuous systems.

Discrete systems
The type of systems whose input and output both are discrete signals or digital signals are called digital systems.
Applications of Digital Image Processing
Some of the major fields in which digital image processing is widely used are mentioned below
• Image sharpening and restoration
• Medical field
• Remote sensing
• Transmission and encoding
• Machine/Robot vision
• Color processing
• Pattern recognition
• Video processing
• Microscopic Imaging

0 Comments