What is DBMS?
- A Database Management System (DBMS) is a collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to access those data.
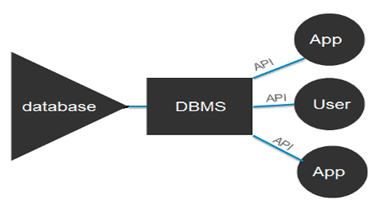
- Database management systems (DBMS) are computer software applications that interact with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data.
Purpose of Database Systems
- The collection of data, usually referred to as the database , contains information relevant to an enterprise.
- The primary goal of a DBMS is to provide a way to store and retrieve database information that is both convenient and efficient.
- A general-purpose DBMS is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases.
Some application of DBMS
Enterprise Information:
- ◦ Sales: For customer, product, and purchase information.
- ◦ Accounting : For payments, receipts, account balances, assets and other Accounting information.
- ◦ Human resources: For information about employees, salaries, payroll taxes, and for generation of paychecks.
- ◦ Manufacturing: For management of the supply chain and for tracking production of items in factories, inventories of items in warehouses and stores, and orders for items.
- Online retailers: For sales data noted above plus online order tracking, generation of recommendation lists, and maintenance of online product evaluations.
Banking and Finance
- ◦ Banking: For customer information, accounts, loans, and banking transactions.
- ◦ Credit card transactions : For purchases on credit cards and generation of monthly statements.
- ◦ Finance: For storing information about holdings, sales, and purchases of financial instruments such as stocks and bonds; also for storing real-time market data to enable online trading by customers and automated trading by the firm.
- Universities : For student information, course registrations, and grades (in addition to standard enterprise information such as human resources and accounting).
- Airlines: For reservations and schedule information. Airlines were among the first to use databases in a geographically distributed manner.
- Telecommunication : For keeping records of calls made, generating monthly bills, maintaining balances on prepaid calling cards, and storing information about the communication networks.
University Database Example
- Application program examples
- Add new students, instructors, and courses
- Register students for courses, and generate class rosters
- Assign grades to students, compute grade point averages (GPA) and generate transcripts
- In the early days, database applications were built directly on top of file systems.
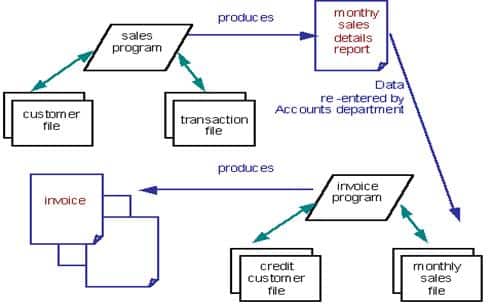
File-processing system
- A file processing system is a collection of files and programs that access/modify these files. Typically, new files and programs are added over time (by different programmers) as new information needs to be stored and new ways to access information are needed.
- This typical file-processing system is supported by a conventional operating system.
- The system stores permanent records in various files,
- It needs different application programs to extract records from, and add records to, the appropriate files.
Disadvantages File-processing system
Major disadvantages of file processing system
- Data redundancy and inconsistency .
- Difficulty in accessing data.
- Data isolation.
- Integrity problems .
- Atomicity problems
- Concurrent-access anomalies.
- Security problem
Drawbacks of using file systems
- Data redundancy and inconsistency
- Multiple file formats, duplication of information in different files
- Difficulty in accessing data
- Need to write a new program to carry out each new task
- Data isolation — multiple files and formats
- Integrity problems
- Integrity constraints (e.g., account balance > 0) become “buried” in program code rather than being stated explicitly
- Hard to add new constraints or change existing ones
- Atomicity of updates
- Failures may leave database in an inconsistent state with partial updates carried out
- Example: Transfer of funds from one account to another should either complete or not happen at all
- Concurrent access by multiple users
- Concurrent access needed for performance
- Uncontrolled concurrent accesses can lead to inconsistencies
- Example: Two people reading a balance (say 100) and updating it by withdrawing money (say 50 each) at the same
- Security problems
- Hard to provide user access to some, but not all, data
Database systems offer solutions to all the above problems
Vi e w o f D a t a
- A major purpose of a database system is to provide users with an abstract view of the data.
- That is, the system hides certain details of how the data are stored and maintained.
Levels of Abstraction
- Since many database-system users are not computer trained, developers hide the complexity from users through several levels of abstraction, to simplify users interactions with the system.
- Physical level: The lowest level of abstraction describes how the data are stored. The physical level describes complex low-level data structures in detail.
- Logical level: The next-higher level of abstraction describes what data are stored in the database, and what relationships exist among those data. The logical level thus describes the entire database in terms of a small number of relatively simple structures. Database administrators, who must decide what information to keep in the database, use the logical level of abstraction.
- View level: The highest level of abstraction describes only part of the entire database. The view level of abstraction exists to simplify their interaction with the system. The system may provide many views for the same database.
- Physical level: describes how a record (e.g., customer) is stored.
- Logical level: describes data stored in database, and the relationships among the data.
type instructor = record
ID : string;
name : string;
dept_name : string;
salary : integer;
end;
- View level: application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information (such as an employee’s salary) for security purposes.
View of Data
+——————-+ +——————-+ +——————-+
| View 1 | | View 2 | … | View n |
+——————-+ +——————-+ +——————-+
| | |
v v v
+————————————————————-+
| Logical Level |
| – Entities |
| – Relationships |
| – Constraints |
+————————————————————-+
|
v
+————————————————————-+
| Physical Level |
| – Storage Structures |
| – Access Methods |
| – Indexing |
+————————————————————-+
An architecture for a database system
Instances and Schemas
- Schema – The overall design of the database is called database schema. In short “the logical structure of the database”
- Example: The database consists of information about a set of customers and accounts and the relationship between them
- Physical schema: database design at the physical level
- Logical schema: database design at the logical level
- Subschema: database design at the view level which describe different views of the database.
- Instance – The collection of information stored in the database at a particular moment is called an instance of the database. In short “the actual content of the database at a particular point in time”.
- Physical Data Independence – the ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema
- Applications depend on the logical schema
- In general, the interfaces between the various levels and components should be well defined so that changes in some parts do not seriously influence others.

0 Comments