Basics of Wireless Communication:
Wireless communication takes places over free space through RF (radio frequency), one device, Transmitter send signal to other device, Receiver. Two devices (transmitter and receiver) must use same frequency (or channel) to be able to communicate with each other. If a large number of wireless devices communicate at same time, radio frequency can cause interference with each other. Interference increases as no of devices increases.
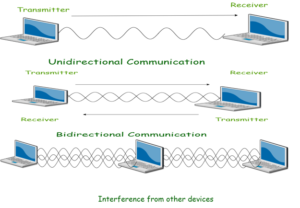
Wireless devices share airtime just like wired devices connect to shared media and share common bandwidth. For effective use of media, all wireless devices operate in half duplex mode to avoid collision or interference. Before the transmission begins, devices following IEEE 802.11 standard must check whether channel is available and clear.
Note: Wireless communication is always half duplex as transmission uses same frequency or channel. To achieve full duplex mode, devices uses different frequency or channel of transmission and
receiving of signals. You can say that wireless communication is Full-duplex but technically it is not.
Radio Frequency:
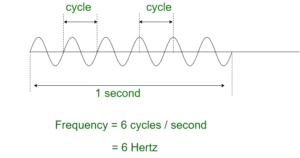
In free space, the sender (transmitter) send an alternating current into a section of wire (an antenna). This sets up a moving electric and magnetic field that away as travelling waves. The electric and magnetic field moves along each other at a right angle to each other as shown. The signal must keep changing or alternating by cycle up and down to keep electric and magnetic field cyclic and pushing forward. The no of cycles a wave taking in a second is called Frequency of the wave.
So,
frequency = no of cycles per second
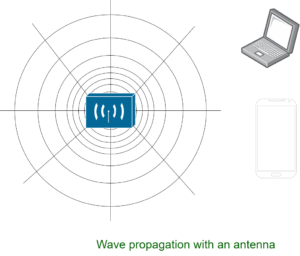
Electromagnetic waves do not travel in a straight line. they travel by expanding in all direction away from antenna. Like you have seen waves travelling in water when you drop or throw a stone in a water body.
Frequency Unit Names :
| Unit | Abbreviation | Meaning |
| Hertz | Hz | Cycles per second |
| Kilohertz | KHz | 1000 Hz |
| Megahertz | MHz | 1, 000, 000 Hz |
| Gigahertz | GHz | 1, 000, 000, 000 Hz |
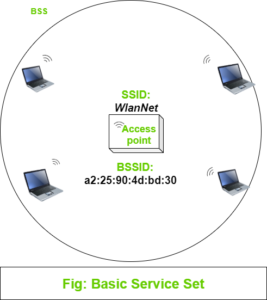
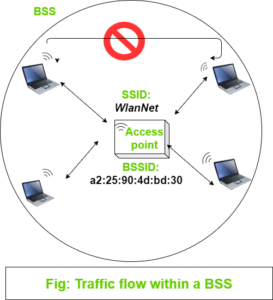
Basic Service Set: We know that wireless communication takes place over the Air. To regulate connection to devices, we need to make every wireless service area a closed group of mobile devices that form around a fixed device. Before mobile devices start data communication, they must advertise their capabilities, and then permission to join should be granted. There is a term defined to such arrangement, IEEE calls this standard a Basic service set (BSS).
At the center of every BSS, there is an access point (AP), it provides services that are necessary to form the infrastructure of Wireless communication. The AP operates in an infrastructure mode and uses a single wireless channel. All devices that want to connect to AP must use that same channel.
Because the operation of BSS depends on AP, BSS is bounded to the area covered by the AP i.e, the area up to which AP’s signal is reachable. This area is called the Basic Service Area (BSA) or cell. The cell is usually a circular shape with the center as AP. The AP serves as a single point of contact for the BSS. The AP uses a unique BSS identifier (BSSID) based on its own MAC address to advertise it’s existence to all devices in the cell.
The AP also advertises a human-readable text string called Service Set identifier (SSID) to uniquely identify the AP. You can say BSSID as a machine-readable unique tag to identify a wireless service and SSID a human-readable service tag.
Membership of mobile devices with BSS is called Association. Once associated, the device becomes a BSS client or an 802.11 station (STA). As long as devices are connected to AP, all data communication passes through AP using BSSID as a source and destination address. You can think why all traffic must pass through AP? They can simply communicate with other devices directly without AP as a middleman. If we don’t do so then the whole point of wireless service will go in vain. Sending data through AP make it stable and controllable.
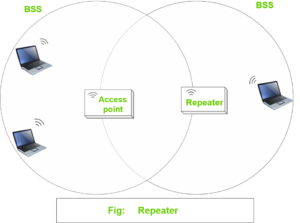
Repeater: An AP in wireless infrastructure usually connected back to the switched networks. BSS has a limited signal coverage area, (BSA). To extend the signal coverage, we can add additional AP but in some scenarios, it is not possible to add additional AP. The solution in such a situation is a Repeater. The repeater is just an AP configured in Repeater mode. A wireless repeater takes a signal as an input and retransmits signals in a new cell around Repeater. The repeater uses two transmitters and receiver to keep the original and repeated signals isolated on a different channel.
Difference between Broadband and Baseband Transmission
| S.No | Baseband Transmission | Broadband Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | In baseband transmission, the type of signalling used is digital. | In broadband transmission, the type of signalling used is analog. |
| 2. | Baseband Transmission is bidirectional in nature. | Broadband Transmission is unidirectional in nature. |
| 3. | Signals can only travel over short distances. | Signals can be travelled over long distances without being attenuated. |
| 4. | It works well with bus topology. | It is used with a bus as well as tree topology. |
| 5. | In baseband transmission, Manchester and Differential Manchester encoding are used. | Only PSK encoding is used. |

0 Comments