Modem Modulator and Demodulator
A modem may refer to any of the following:
- A modem or broadband modem is a hardware device that connects a computer or router to a broadband. For example, a cable modem and DSL modem are two examples of these types of Modems.
- Today, a “modem” is most often used to describe a broadband modem. However, it also describes what was initially considered a modem (described below) to connect to the Internet. To help prevent confusion, use the terms “broadband modem” and “dial-up modem.”
- A broadband modem is an external device that connects to your computers and other network devices using either a network cable or over a wireless connection.
- Short for modulator/demodulator, a modem is a hardware device that allows a computer to send and receive information over telephone lines. When sending a signal, the device converts (“modulates”) digital data to an analog audio signal, and transmits it over a telephone line. Similarly, when an analog signal is received, the modem converts it back (“demodulates” it) to a digital signal.
- To help prevent confusion between a broadband modem, you can refer to this modem as a dial-up modem.
Modems are referred to as an asynchronous device, meaning that the device transmits data in an intermittent stream of small packets. Once received, the receiving system then takes the data in the packets and reassembles it into a form the computer can use.
| Stop 1 bit |
Data 8 bits |
Start 1 bit |
Stop 1 bit |
Data 8 bits |
Start 1 bit |
| Packet 10 bits |
Packet 10 bits |
||||
The above chart represents how an asynchronous transmission transmits over a phone line. In asynchronous communication, one byte (eight bits) is transferred within one packet, which is equivalent to one character. However, for the computer to receive this information, each packet must contain a Start and a Stop bit; therefore, the complete packet would be ten bits. The above chart is a transmission of the word HI, which is equivalent to two bytes (16 bits).
Types of computer modems
Below are the four versions of a computer modem found in computers.
Onboard modem – Modem built onto the computer motherboard. These modems cannot be removed, but can be disabled through a jumper or BIOS setup.
Internal modem – Modem that connects to a PCI slot inside a newer desktop computer, or ISA slot on an older computer. The internal modem shown above is an example of a PCI modem.
External modem – Modem in a box that connects to the computer externally, using a serial port or USB port. The picture is an example of an external US Robotics modem.
Removable modem – Modem used with older laptops PCMCIA slot and can be added or removed as needed.
Telephone Modem
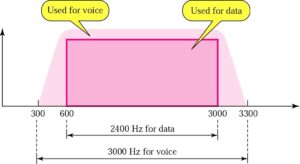
- A telephone line has a bandwidth of almost 2400 Hz for data transmission (600 – 3000 Hz). This bandwidth defines a baseband nature which needs to modulate for data transmission – modem. Modem – modulator and demodulator

Telephone Line Bandwidth
If a telephone system is to be operated as a cloud service through an Internet connection, the bandwidth of the connection is the main factor in determining the maximum possible number of parallel calls. It is important that sufficient bandwidth is available for the total number of possible simultaneous voice channels, in both directions of transmission. With ADSL connections, which have low upload data rates compared to the download data rates, the upload bandwidth is the limiting factor of such a system.
Traditional Modems
The functionality provided by a traditional dialup modem—the ability to send and receive information electronically—is also offered in other technologies that offer faster transmission speeds, although each is not without its disadvantages. Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Lines (ADSL), and Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL) all use more capacity of the existing phone to provide services.
At 128K, ISDN is more than twice as fast as a dialup modem, but not nearly as fast as ADSL or DSL. ADSL can deliver data at 8mbps, but is available only in selected urban areas. DSL transmits at a high rate of speed, but to ensure reliable service, the user must be located near the phone company’s central office. In addition, a DSL connection is always “on,” and so makes a computer more vulnerable to attacks from hackers. To secure a DSL connection, a user should install either a software package called a firewall or a piece of hardware called a router. With either of these in place, the DSL connection cannot be detected by outsiders.
56K Modem: V.90
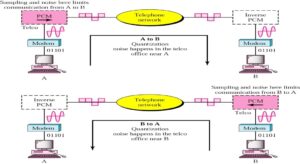
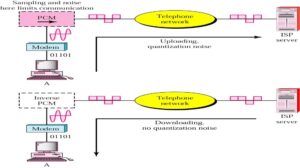
The V.90 modem is the latest technology to offer faster Internet connection speeds without requiring that consumers subscribe to more expensive digital line services. Before V.90 technology, modems were theoretically limited to about 35 Kbps by the quantization noise that affects analog to digital conversions . However, in today’s world of increasing digital transmission facilities it is safe to assume that an increasing number of Internet service providers (ISPs) are digitally connected both to the Internet and to a telephone company’s central office (CO). When this is the case, there is a clear digital connection downstream from the ISP’s modem to the CO’s line card that serves the user and contains a digital to analog converter. The result of having this digital connection is that an analog to digital conversion (and therefore quantization noise) is avoided between ISP and CO. Without the limits imposed by quantization noise, it is theoretically possible to achieve downstream connection speeds of up to 64 Kbps. Practically, however, this is not yet possible. Performance barriers such as µ-law quantization reduce the effective data rate of V.90 modems to a maximum of 56 Kbps downstream. In the downstream direction, the V.90 modem operates using pulse amplitude modulation (PAM).
- Max: 56Kbps
- 8000 samples/s, 8 bits/sample,
- 7bits per data => 56Kbps
- 56K Modem: V.92
- Similar to V.90
- Modem can adjust speed
- If noise allows => upload max 48 Kbps, download still 56 Kbps.
- 92: can interrupt the Internet connection when there is an incoming call (if call-waiting service is installed)
Types of Transmission Media
In data communication a transmission medium is the channel through which data is sent from one place to another. Transmission Media is broadly classified into the following types:
- Guided Media:
It is also denoted to as Wired or Bounded transmission media. Signals being transmitted are directed and confined in a narrow pathway by using physical links.
Features:
- High Speed
- Secure
- Used for comparatively shorter distances
There are 3 major types of Guided Media:
(i) Twisted Pair Cable :
It consists of 2 separately insulated conductor wires wound about each other. Generally, several such pairs are bundled together in a protective sheath. They are the most widely used Transmission Media. Twisted Pair is of two types:
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
UTP consists of two insulated copper wires twisted around one another. This type of cable has the ability to block interference and does not depend on a physical shield for this purpose. It is used for telephonic applications.
Advantages:
⇢ Least expensive
⇢ Easy to install
⇢ High-speed capacity
⇢ Susceptible to external interference
⇢ Lower capacity and performance in comparison to STP
⇢ Short distance transmission due to attenuation
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
This type of cable consists of a special jacket (a copper braid covering or a foil shield) to block external interference. It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and in voice and data channels of telephone lines.
Advantages:
- Better performance at a higher data rate in comparison to UTP
- Eliminates crosstalk
- Comparatively faster
- Comparatively difficult to install and manufacture
- More expensive
- Bulky
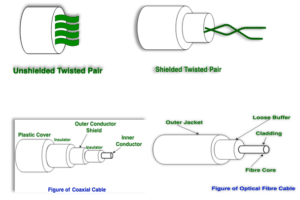
(ii) Coaxial Cable :
It has an outer plastic covering containing an insulation layer made of PVC or Teflon. Additionally, it has two parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover. The coaxial cable transmits information in two modes: Baseband mode (dedicated cable bandwidth) and Broadband mode (cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges). Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables.
Advantages:
- High Bandwidth
- Better noise Immunity
- Easy to install and expand
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages:
- Single cable failure can disrupt the entire network
(iii) Optical Fiber Cable :
It uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding. It is used for the transmission of large volumes of data. The cable can be unidirectional or bidirectional. The WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexer) supports two modes, namely unidirectional and bidirectional mode.
Advantages:
- Increased capacity and bandwidth
- Lightweight
- Less signal attenuation
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference
- Resistance to corrosive materials
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to install and maintain
- High cost
- Fragile
(iv) Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of the planar transmission line. It uses a conducting material to transmit high-frequency waves it is also called a waveguide. This conducting material is sandwiched between two layers of the ground plane which are usually shorted to provide EMI immunity.
(v) Microstripline
In this, the conducting material is separated from the ground plane by a layer of dielectric.
- Unguided Media:
It is also referred to as Wireless or Unbounded transmission media. No physical medium is required for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
Features:
- The signal is broadcasted through air
- Less Secure
- Used for larger distances
There are 3 types of Signals transmitted through unguided media:
(i) Radio waves :
These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. The sending and receiving antennas need not be aligned. Frequency Range:3KHz : 1GHz. AM and FM radios and cordless phones use Radio waves for transmission.
Further Categorized as (i) Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
(ii) Microwaves
It is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance covered by the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna. Frequency Range: 1GHz : 300GHz. These are majorly used for mobile phone communication and television distribution.
(iii) Infrared:
Infrared waves are used for very short distance communication. They cannot penetrate through obstacles. This prevents interference between systems. Frequency Range: 300GHz : 400THz. It is used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, keyboard, printer, etc.

0 Comments