Data Communications
Data Communications : Data Communication is the exchange of data (in the form of 0’s and 1’s) between two devices via some form of transmission medium (such a cable).
In other way can define, Data Communication is a process of exchanging data or information. In case of computer networks this exchange is done between two devices over a transmission medium. This process involves a communication system which is made up of hardware and software. The hardware part involves the sender and receiver devices and the intermediate devices through which the data passes. The software part involves certain rules which specify what is to be communicated, how it is to be communicated and when. It is also called as a Protocol. The following sections describes the fundamental characteristics that are important for the effective working of data communication process and is followed by the components that make up a data communications system.
What is important?
-
- Delivery (deliver data to the correct destination)
- Accuracy (must deliver the data accurately, no altered data in transmission)
Timeliness (deliver data in timely manner, data delivered late are useless)
Aspects of Data Communications
- Components
- Data representation
- Direction of data flow
Components of a Communication System
- Message:
The message is the information (or data) to be transmitted. For example, text, numbers, pictures, sound, video, or any combination of these.
- Sender:
sender is the device that sends the data message. It can be a computer, telephone, video camera, and so on.
- Receiver:
The receiver is the device that receives the message.
- Medium (Channel): The transmission medium is the physical path by which a message travels from the sender to receiver. For example twisted pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, radio waves (terrestrial or satellite microwaves).
- Protocol:
A protocol is a set of rules that govern data communication. It represents an agreement between the communicating devices.
Characteristics of Data Communication
The effectiveness of any data communications system depends upon the following four fundamental characteristics:
1. Delivery:
data should be delivered to the correct destination and correct user.
2. Accuracy:
The communication system should deliver the data accurately, without introducing any errors. The data may get corrupted during transmission affecting the accuracy of the delivered data.
3. Timeliness:
Audio and Video data has to be delivered in a timely manner without any delay; such a data delivery is called real time transmission of data.
4. Jitter:
It is the variation in the packet arrival time. Uneven Jitter may affect the timeliness of data being transmitted.
Data Representation
Data is collection of raw facts which is processed to deduce information.
There may be different forms in which data may be represented. Some of the forms of data used in communications are as follows:
-
- Text
Text includes combination of alphabets in small case as well as upper case. It is stored as a pattern of bits. Prevalent encoding system : ASCII, Unicode - Numbers
Numbers include combination of digits from 0 to 9. It is stored as a pattern of bits. Prevalent encoding system :
ASCII, Unicode - Images
An image is worth a thousand words‖ is a very famous saying. In computers images are digitally stored. - Pixel
- Text
A Pixel is the smallest element of an image. To put it in simple terms, a picture or image is a matrix of pixel elements. The pixels are represented in the form of bits. Depending upon the type of image (black n white or color) each pixel would require different number of bits to represent the value of a pixel. The size of an image depends upon the number of pixels (also called resolution) and the bit pattern used to indicate the value of each pixel.
Example: if an image is purely black and white (two color) each pixel can be represented by a value either 0 or 1, so an image made up of 10 x 10 pixel elements would require only 100 bits in memory to be stored. On the other hand an image that includes gray may require 2 bits to represent every pixel value (00 – black, 01 – dark gray, 105 light gray, 11 –white). So the same 10 x 10 pixel image would now require 200 bits of memory to be stored. Commonly used Image formats : jpg, png, bmp, etc
- Audio
Data can also be in the form of sound which can be recorded and broadcasted. Example: What we hear on the radio is a source of data or information. Audio data is continuous, not discrete.
- Video
Video refers to broadcasting of data in form of picture or movie.
DATA FLOW
Two devices communicate with each other by sending and receiving data. The data can flow between the two devices in the following ways.
1. Simplex
2. Half Duplex
3. Full Duplex
Simplex
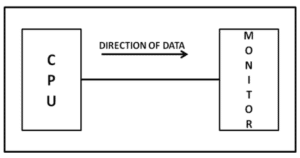
Figure: Simplex mode of communication
Simplex:
In simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, as on a one-way street. Only one of the two devices on a link can transmit; the other can only receive which can be represented in the following figure. Keyboards and traditional monitors are examples of simplex devices. In Simplex, communication is unidirectional. Only one of the devices sends the data and the other one only receives the data.
Example: in the above diagram: a cpu send data while a monitor only receives data.
Half Duplex
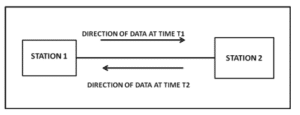
Figure: Half Duplex Mode of Communication
Half-Duplex:
In half-duplex mode, each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice versa which will represent in the following figure. The half-duplex mode is used in cases where there is no need for communication in both directions at the same time; the entire capacity of the channel can be utilized for each direction.
In half duplex both the stations can transmit as well as receive but not at the same time. When one device is sending other can only receive and vice versa (as shown in figure above.)
Example: A walkie-talkie.
Full Duplex
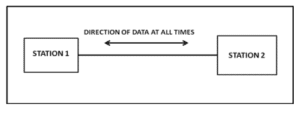
Figure: Full Duplex Mode of Communication
Full-Duplex:
In full-duplex mode (also called duplex), both stations can transmit and receive simultaneously as shown in the following figure. One common example of full-duplex communication is the telephone network. When two people are communicating by a telephone line, both can talk and listen at the same time. The full-duplex mode is used when communication in both directions is required all the time. Example: mobile phones. both stations can transmit and receive at the same time.
PROTOCOL
A Protocol is one of the components of a data communications system. Without protocol communication cannot occur. The sending device cannot just send the data and expect the receiving device to receive and further interpret it correctly. When the sender sends a message it may consist of text, number, images, etc. which are converted into bits and grouped into blocks to be transmitted and often certain additional information called control information is also
added to help the receiver interpret the data. For successful communication to occur, the sender and receiver must agree upon certain rules called protocol.
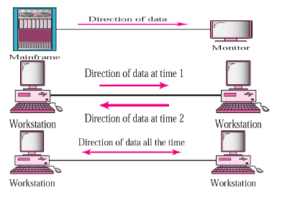
Direction of Data Flow

0 Comments