Computer Fundamentals
Computer is an advanced electronic device that takes raw data as an input from the user and processes it under the control of a set of instructions (called program), produces a result (output), and saves it for future use. This tutorial explains the foundational concepts of computer hardware, software, operating systems, peripherals, etc. along with how to get the most value and impact from computer technology.
Functionalities of a Computer
If we look at it in a very broad sense, any digital computer carries out the following five functions −
Step 1 − Takes data as input.
Step 2 − Stores the data/instructions in its memory and uses them as required.
Step 3 − Processes the data and converts it into useful information.
Step 4 − Generates the output.
Step 5 − Controls all the above four steps.

Advantages of Computers
Following are certain advantages of computers.
High Speed
- Computer is a very fast device.
- It is capable of performing calculation of very large amount of data.
- The computer has units of speed in microsecond, nanosecond, and even the picosecond.
- It can perform millions of calculations in a few seconds as compared to man who will spend many months to perform the same task.
Accuracy
- In addition to being very fast, computers are very accurate.
- The calculations are 100% error free.
- Computers perform all jobs with 100% accuracy provided that the input is correct.
Storage Capability
- Memory is a very important characteristic of computers.
- A computer has much more storage capacity than human beings.
- It can store large amount of data.
- It can store any type of data such as images, videos, text, audio, etc.
Diligence
- Unlike human beings, a computer is free from monotony, tiredness, and lack of concentration.
- It can work continuously without any error and boredom.
- It can perform repeated tasks with the same speed and accuracy.
Versatility
- A computer is a very versatile machine.
- A computer is very flexible in performing the jobs to be done.
- This machine can be used to solve the problems related to various fields.
- At one instance, it may be solving a complex scientific problem and the very next moment it may be playing a card game.
Reliability
- A computer is a reliable machine.
- Modern electronic components have long lives.
- Computers are designed to make maintenance easy.
Automation
- Computer is an automatic machine.
- Automation is the ability to perform a given task automatically. Once the computer receives a program i.e., the program is stored in the computer memory, then the program and instruction can control the program execution without human interaction.
Reduction in Paper Work and Cost
- The use of computers for data processing in an organization leads to reduction in paper work and results in speeding up the process.
- As data in electronic files can be retrieved as and when required, the problem of maintenance of large number of paper files gets reduced.
- Though the initial investment for installing a computer is high, it substantially reduces the cost of each of its transaction.
Disadvantages of Computers
Following are certain disadvantages of computers.
No I.Q.
- A computer is a machine that has no intelligence to perform any task.
- Each instruction has to be given to the computer.
- A computer cannot take any decision on its own.
Dependency
- It functions as per the user’s instruction, thus it is fully dependent on humans.
Environment
- The operating environment of the computer should be dust free and suitable.
No Feeling
- Computers have no feelings or emotions.
- It cannot make judgment based on feeling, taste, experience, and knowledge unlike humans.
History of Computers
The first counting device was used by the primitive people. They used sticks, stones and bones as counting tools. As human mind and technology improved with time more computing devices were developed. Some of the popular computing devices starting with the first to recent ones are described below;
Abacus
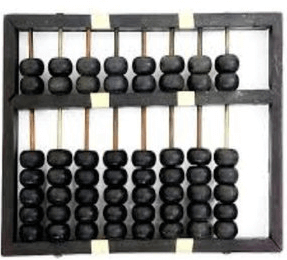
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.
It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. Abacus is still used in some countries like China, Russia and Japan. An image of this tool is shown below;
Napier’s Bones
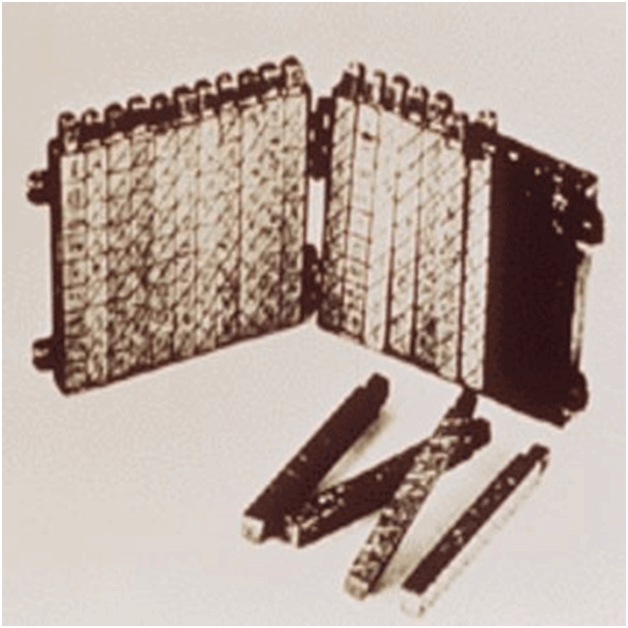
It was a manually-operated calculating device which was invented by John Napier (1550-1617) of Merchiston. In this calculating tool, he used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide. So, the tool became known as “Napier’s Bones. It was also the first machine to use the decimal point.
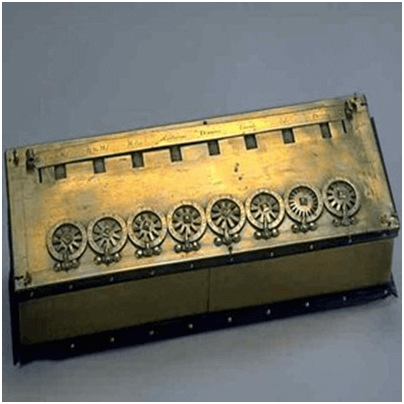
Pascaline
Pascaline is also known as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician-philosopher Biaise Pascal. It is believed that it was the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
Pascal invented this machine to help his father, a tax accountant. It could only perform addition and subtraction. It was a wooden box with a series of gears and wheels. When a wheel is rotated one revolution, it rotates the neighboring wheel. A series of windows is given on the top of the wheels to read the totals. An image of this tool is shown below;
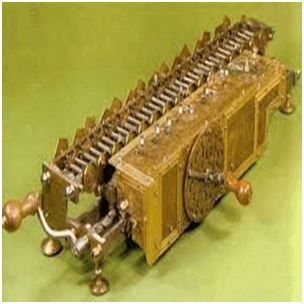
Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel
It was developed by a German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz in 1673. He improved Pascal’s invention to develop this machine. It was a digital mechanical calculator which was called the stepped reckoner as instead of gears it was made of fluted drums. See the following image;
Difference Engine
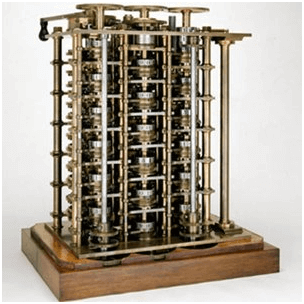
In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as “Father of Modern Computer”. It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations. It was a steam driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.
Analytical Engine
This calculating machine was also developed by Charles Babbage in 1830. It was a mechanical computer that used punch-cards as input. It was capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory.

Tabulating Machine
It was invented in 1890, by Herman Hollerith, an American statistician. It was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards. It could tabulate statistics and record or sort data or information. This machine was used in the 1890 U.S. Census. Hollerith also started the Hollerith?s Tabulating Machine Company which later became International Business Machine (IBM) in 1924.

Differential Analyzer
It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine has vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations. It could do 25 calculations in few minutes.
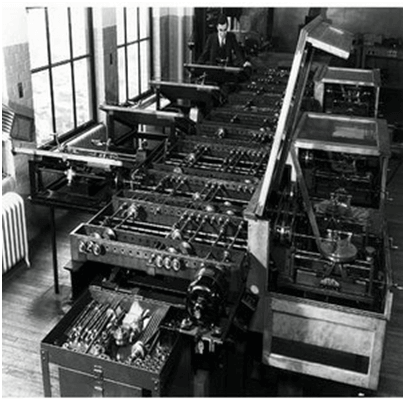
Mark I
The next major changes in the history of computer began in 1937 when Howard Aiken planned to develop a machine that could perform calculations involving large numbers. In 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard. It was the first programmable digital computer.

Generations of Computers
A generation of computers refers to the specific improvements in computer technology with time. In 1946, electronic pathways called circuits were developed to perform the counting. It replaced the gears and other mechanical parts used for counting in previous computing machines.
In each new generation, the circuits became smaller and more advanced than the previous generation circuits. The miniaturization helped increase the speed, memory and power of computers. There are five generations of computers which are described below;
First Generation Computers
The first generation (1946-1959) computers were slow, huge and expensive. In these computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory. These computers were mainly depended on batch operating system and punch cards. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices in this generation;
Some of the popular first generation computers are;
- ENIAC ( Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- EDVAC ( Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
- UNIVACI( Universal Automatic Computer)
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
Second Generation Computers
The second generation (1959-1965) was the era of the transistor computers. These computers used transistors which were cheap, compact and consuming less power; it made transistor computers faster than the first generation computers.
In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic disc and tapes were used as the secondary storage. Assembly language and programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers.
Some of the popular second generation computers are;
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers
The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors. A single IC can pack huge number of transistors which increased the power of a computer and reduced the cost. The computers also became more reliable, efficient and smaller in size. These generation computers used remote processing, time-sharing, multi programming as operating system. Also, the high-level programming languages like FORTRON-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, ALGOL-68 were used in this generation.
Some of the popular third generation computers are;
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP(Personal Data Processor)
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation Computers
The fourth generation (1971-1980) computers used very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits; a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements. These chips made this generation computers more compact, powerful, fast and affordable. These generation computers used real time, time sharing and distributed operating system. The programming languages like C, C++, DBASE were also used in this generation.
Some of the popular fourth generation computers are;
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers
In fifth generation (1980-till date) computers, the VLSI technology was replaced with ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration). It made possible the production of microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components. This generation computers used parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. The programming languages used in this generation were C, C++, Java, .Net, etc.
Some of the popular fifth generation computers are;
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- UltraBook
- ChromeBook

0 Comments