Flowchart
Flowchart is a diagrammatic representation of sequence of logical steps of a program. Flowcharts use simple geometric shapes to depict processes and arrows to show relationships and process/data flow.
Flowchart Symbols
Here is a chart for some of the common symbols used in drawing flowcharts.
| Symbol | Symbol Name | Purpose |
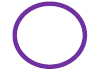
| Start/Stop |
|
|
| Process |
|
|
| Input/ Output | Used for denoting program inputs and outputs. | |
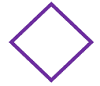 |
Decision |
|
 |
Arrow |
|
 |
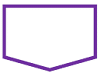
On-page Connector | Connects two or more parts of a flowchart, which are on the same page. |
 |
Off-page Connector | Connects two parts of a flowchart which are spread over different pages. |
Guidelines for Developing Flowcharts
These are some points to keep in mind while developing a flowchart −
- Flowchart can have only one start and one stop symbol
- On-page connectors are referenced using numbers
- Off-page connectors are referenced using alphabets
- General flow of processes is top to bottom or left to right
- Arrows should not cross each other
Example Flowcharts
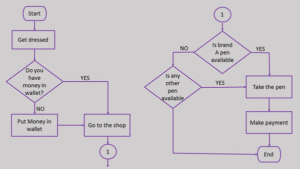
Here is the flowchart for going to the market to purchase a pen.
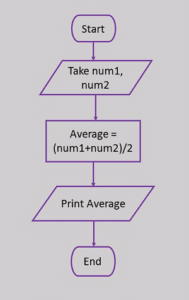
Here is a flowchart to calculate the average of two numbers.
Intermediate & Advanced Flowchart Symbols
As you know, flowcharts are made up of a sequence of actions, data, services, and/or materials. They illustrate where data is being input and output, where information is being stored, what decisions need to be made, and which people need to be involved. In addition the basic flowchart conventions, rules, and symbols, these intermediate flowchart symbols will help you describe your process with even more detail.
Document Symbols
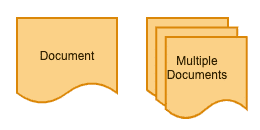
Single and multiple document icons show that there are additional points of reference involved in your flowchart. You might use these to indicate items like “create an invoice” or “review testing paperwork.”
Data Symbols
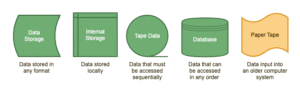
Data symbols clarify where the data your flowchart references is being stored. (You probably won’t use the paper tape symbol, but it definitely came in handy back in the day.)
Input & Output Symbols
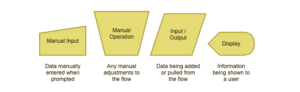
Input and output symbols show where and how data is coming in and out throughout your process.
Merging & Connecting Symbols
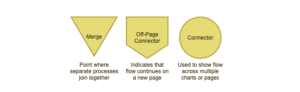
Agreed-upon merging and connector symbols make it easier to connect flowcharts that span multiple pages.
Additional Useful Flowchart Symbols
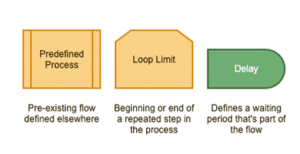
The above are a few additional symbols that prove your flowcharting prowess when put to good use.

0 Comments