Programming Methodologies
When programs are developed to solve real-life problems like inventory management, payroll processing, student admissions, examination result processing, etc. they tend to be huge and complex. The approach to analyzing such complex problems, planning for software development and controlling the development process is called programming methodology.
Types of Programming Methodologies
There are many types of programming methodologies prevalent among software developers −
Procedural Programming
Problem is broken down into procedures, or blocks of code that perform one task each. All procedures taken together form the whole program. It is suitable only for small programs that have low level of complexity.
Procedural programming is widely used in large-scale projects, when the following benefits are important:
- re-usability of pieces code designed as procedures
- ease of following the logic of program;
- Maintainability of code.
- Emphasis is on doing things (algorithms).
- Most of the functions share global data.
- Data move openly around the system from function to function.
- Functions transform data from one form to another.Procedural programming is a sub-paradigm of imperative programming, since each step of computation is described explicitly, even if by the means of defining procedures.
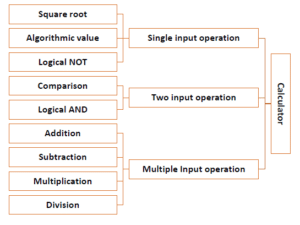
Example − For a calculator program that does addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, square root and comparison, each of these operations can be developed as separate procedures. In the main program each procedure would be invoked on the basis of user’s choice.
Object-oriented Programming
Here the solution revolves around entities or objects that are part of problem. The solution deals with how to store data related to the entities, how the entities behave and how they interact with each other to give a cohesive solution.
Some of the features of object oriented programming are:
• Emphasis is on data rather than procedure.
• Programs are divided into what are known as objects.
• Data structures are designed such that they characterize the objects.
• Functions that operate on the data of an object are ties together in the data
structure.
• Data is hidden and cannot be accessed by external function.
• Objects may communicate with each other through function.
• New data and functions can be easily added whenever necessary.
• Follows bottom up approach in program design.
Example − If we have to develop a payroll management system, we will have entities like employees, salary structure, leave rules, etc. around which the solution must be built.
Functional Programming
Here the problem, or the desired solution, is broken down into functional units. Each unit performs its own task and is self-sufficient. These units are then stitched together to form the complete solution.
Example − A payroll processing can have functional units like employee data maintenance, basic salary calculation, gross salary calculation, leave processing, loan repayment processing, etc.
Logical Programming
Here the problem is broken down into logical units rather than functional units. Example: In a school management system, users have very defined roles like class teacher, subject teacher, lab assistant, coordinator, academic in-charge, etc. So the software can be divided into units depending on user roles. Each user can have different interface, permissions, etc.
Algorithm Approaches
Software developers may choose one or a combination of more than one of these methodologies to develop a software. Note that in each of the methodologies discussed, problem has to be broken down into smaller units. To do this, developers use any of the following two approaches −
- Top-down approach
- Bottom-up approach
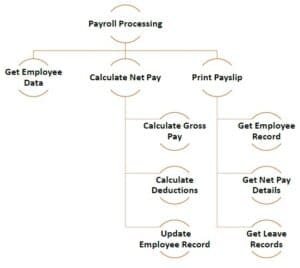
Top-down or Modular Approach
The problem is broken down into smaller units, which may be further broken down into even smaller units. Each unit is called a module. Each module is a self-sufficient unit that has everything necessary to perform its task.
The following illustration shows an example of how you can follow modular approach to create different modules while developing a payroll processing program.
Bottom-up Approach
In bottom-up approach, system design starts with the lowest level of components, which are then interconnected to get higher level components. This process continues till a hierarchy of all system components is generated. However, in real-life scenario it is very difficult to know all lowest level components at the outset. So bottoms up approach is used only for very simple problems.
Let us look at the components of a calculator program.
Programming methodology deals with the analysis, design and implementation of programs.
Algorithm
Algorithm is a step-by-step finite sequence of instruction, to solve a well-defined computational problem. That is, in practice to solve any complex real life problems;
First, we have to define the problems.
Second, step is to design the algorithm to solve that problem.
Writing and executing programs and then optimizing them may be effective for small programs. Optimization of a program is directly concerned with algorithm design. But for a large program, each part of the program must be well organized before writing the program. There are few steps of refinement involved when a problem is converted to program; this method is called stepwise refinement method. There are two approaches for algorithm design; they are top-down and bottom-up algorithm design.
Stepwise Refinement Techniques
We can write an informal algorithm, if we have an appropriate mathematical model for a problem. The initial version of the algorithm will contain general statements, i.e., informal instructions. Then we convert this informal algorithm to formal algorithm, that is, more definite instructions by applying any programming language syntax and semantics partially. Finally a program can be developed by converting the formal algorithm by a programming language manual. From the above discussion we have understood that there are several steps to reach a program from a mathematical model. In every step there is a refinement (or conversion). That is to convert an informal algorithm to a program, we must go through several stages of formalization until we arrive at a program — whose meaning is formally defined by a programming language manual — is called stepwise refinement techniques.
There are three steps in refinement process, which is illustrated in following Figure
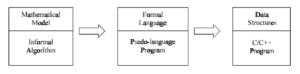
- In the first stage, modeling, we try to represent the problem using an appropriate mathematical model such as a graph, tree etc. At this stage, the solution to the problem is an algorithm expressed very informally.
- At the next stage, the algorithm is written in pseudo-language (or formal algorithm) that is, a mixture of any programming language constructs and less formal English statements. The operations to be performed on the various types of data become fixed.
- In the final stage we choose an implementation for each abstract data type and write the procedures for the various operations on that type. The remaining informal statements in the pseudo-language algorithm are replaced by (or any programming language) C/C++ code.

0 Comments