MIS Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Business Continuity Planning BCPBCP or Business Continuity and Resiliency
Planning BCRPBCRP creates a guideline for continuing business operations under adverse conditions such as a natural calamity, an interruption in regular business processes, loss or damage to critical infrastructure, or a crime done against the business.
It is defined as a plan that “identifies an organization’s exposure to internal and external threats and synthesizes hard and soft assets to provide effective prevention and recovery for the organization, while maintaining competitive advantage and value system integrity.”
Understandably, risk management and disaster management are major components in business continuity planning.
Objectives of BCP
Following are the objectives of BCP:
- Reducing the possibility of any interruption in regular business processes using proper risk management.
- Minimizing the impact of interruption, if any.
- Teaching the staff their roles and responsibilities in such a situation to safeguard their own security and other interests.
- Handling any potential failure in supply chain system, to maintain the natural flow of business.
- Protecting the business from failure and negative publicity.
- Protecting customers and maintaining customer relationships.
- Protecting the prevalent and prospective market and competitive advantage of the business.
- Protecting profits, revenue and goodwill.
- Setting a recovery plan following a disruption to normal operating conditions. Fulfilling legislative and regulatory requirements.
Traditionally a business continuity plan would just protect the data center. With the advent of technologies, the scope of a BCP includes all distributed operations, personnel, networks, power and eventually all aspects of the IT environment.
Phases of BCP
The business continuity planning process involves recovery, continuation, and preservation of the entire business operation, not just its technology component. It should include contingency plans to protect all resources of the organization, e.g., human resource, financial resource and IT infrastructure, against any mishap.
It has the following phases:
- Project management & initiation
- Business Impact Analysis BIABIA
- Recovery strategies
- Plan design & development
- Testing, maintenance, awareness, training
Project Management and Initiation
This phase has the following sub-phases:
- Establish need riskanalysisriskanalysis
- Get management support
- Establish team functional,technical,BCC−BusinessContinuityCoordinatorfunctional,technical,BCC−Bus inessContinuityCoordinator
- Create work plan scope, goals, methods, timeline scope, goals, methods, timeline
- Initial report to management
- Obtain management approval to proceed
Business Impact Analysis
This phase is used to obtain formal agreement with senior management for each timecritical business resource. This phase has the following sub-phases:
- Deciding maximum tolerable downtime, also known as MAO Maximum Allowable
Outage Maximum Allowable Outage
- Quantifying loss due to business outage financial,extracostofrecovery,embarrassmentfinancial,extracostofrecovery,embarrassme nt, without estimating the probability of kinds of incidents, it only quantifies the consequences
- Choosing information gathering methods surveys,interviews,softwaretoolssurveys,interviews,softwaretools
- Selecting interviewees
- Customizing questionnaire
- Analyzing information
- Identifying time-critical business functions
- Assigning MTDs
- Ranking critical business functions by MTDs
- Reporting recovery options
- Obtaining management approval
Recovery Phase
This phase involves creating recovery strategies are based on MTDs, predefined and management-approved. These strategies should address recovery of:
- Business operations
- Facilities & supplies
- Users workersandend−usersworkersandend−users
- Network
- Data center technical
- Data off−sitebackupsofdataandapplicationsoff−sitebackupsofdataandapplications
BCP Development Phase
This phase involves creating detailed recovery plan that includes:
- Business & service recovery plans
- Maintenance plan
- Awareness & training plan
- Testing plan
The Sample Plan is divided into the following phases:
- Initial disaster response
- Resume critical business ops
- Resume non-critical business ops
- Restoration return to primary site return to primary site
- Interacting with external groups customers,media,emergencyresponderscustomers,media,emergencyresponders
Final Phase
The final phase is a continuously evolving process containing testing maintenance, and training.
The testing process generally follows procedures like structured walk-through, creating checklist, simulation, parallel and full interruptions.
Maintenance involves:
- Fixing problems found in testing
- Implementing change management
- Auditing and addressing audit findings
- Annual review of plan
Training is an ongoing process and it should be made a part of the corporate standards and the corporate culture.
Supply Chain Management SCM
Supply chain management is the systemic, strategic coordination of the traditional business functions and tactics across these business functions – both within a particular company and across businesses within the supply chain- all coordinated to improve the long-term performance of the individual companies and the supply chain as a whole.
In a traditional manufacturing environment, supply chain management meant managing movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-progress inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
It involves managing the network of interconnected smaller business units, networks of channels that take part in producing a merchandise of a service package required by the end users or customers.
With businesses crossing the barriers of local markets and reaching out to a global scenario, SCM is now defined as:
Design, planning, execution, control, and monitoring of supply chain activities with the objective of creating net value, building a competitive infrastructure, leveraging worldwide logistics, synchronizing supply with demand and measuring performance globally.
SCM consists of:
- operations management
- logistics
- procurement
- information technology
- integrated business operations Objectives of SCM
- To decrease inventory cost by more accurately predicting demand and scheduling production to match it.
- To reduce overall production cost by streamlining production and by improving information flow.
- To improve customer satisfaction.
Features of SCM

Scope of SCM
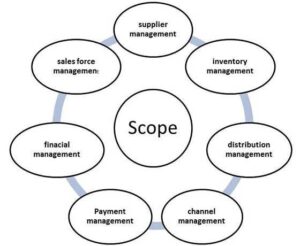
SCM Processes
- Customer Relationship Management
- Customer Service Management
- Demand Management
- Customer Order Fulfillment
- Manufacturing Flow Management
- Procurement Management
- Product Development and Commercialization
- Returns Management
Advantages of SCM
SCM have multi-dimensional advantages:
- To the suppliers:
- Help in giving clear-cut instruction o Online data transfer reduce paper work Inventory Economy:
- Low cost of handling inventory
- Low cost of stock outage by deciding optimum size of replenishment orders o Achieve excellent logistical performance such as just in time Distribution Point:
- Satisfied distributor and whole seller ensure that the right products reach the right place at right time
- Clear business processes subject to fewer errors o Easy accounting of stock and cost of stock Channel Management:
- Reduce total number of transactions required to provide product assortment o Organization is logically capable of performing customization requirements Financial management: o Low cost o Realistic analysis
- Operational performance:
- It involves delivery speed and consistency.
- External customer:
- Conformance of product and services to their requirements o Competitive prices o Quality and reliability o Delivery o After sales services
- To employees and internal customers: o Teamwork and cooperation o Efficient structure and system
Quality work o Delivery

0 Comments