Content Management System (CMS)
A Content Management System CMSCMS allows publishing, editing, and modifying content as well as its maintenance by combining rules, processes and/or workflows, from a central interface, in a collaborative environment.
A CMS may serve as a central repository for content, which could be, textual data, documents, movies, pictures, phone numbers, and/or scientific data.
Functions of Content Management
- Creating content
- Storing content
- Indexing content
- Searching content
- Retrieving content
- Publishing content
- Archiving content
- Revising content
- Managing content end-to-end Content Management Workflow
- Designing content template, for example web administrator designs webpage template for web content management.
- Creating content blocks, for example, a web administrator adds empower CMS tags called “content blocks” to webpage template using CMS.
- Positioning content blocks on the document, for example, web administrator positions content blocks in webpage.
- Authoring content providers to search, retrieve, view and update content.
Advantages of CMS
Content management system helps to secure privacy and currency of the content and enhances performance by:
- Ensuring integrity and accuracy of content by ensuring only one user modifies the content at a time.
- Implementing audit trails to monitor changes made in content over time.
- Providing secured user access to content.
- Organization of content into related groups and folders.
- Allowing searching and retrieval of content.
- Recording information and meta-data related to the content, like author and title of content, version of content, date and time of creating the content etc.
- Workflow based routing of content from one user to another.
- Converting paper-based content to digital format.
- Organizing content into groups and distributing it to target audience.
Executive Support System (ESS)
Executive support systems are intended to be used by the senior managers directly to provide support to non-programmed decisions in strategic management.
These information are often external, unstructured and even uncertain. Exact scope and context of such information is often not known beforehand.
This information is intelligence based:
- Market intelligence
- Investment intelligence
- Technology intelligence
Examples of Intelligent Information
Following are some examples of intelligent information, which is often the source of an ESS:
- External databases
- Technology reports like patent records etc.
- Technical reports from consultants
- Market reports
- Confidential information about competitors
- Speculative information like market conditions
- Government policies
- Financial reports and information
Features of Executive Information System
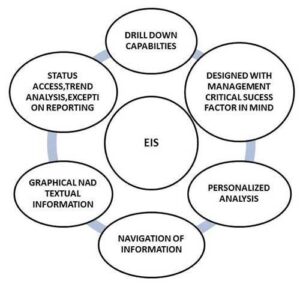
Advantages of ESS
- Easy for upper level executive to use
- Ability to analyze trends
- Augmentation of managers’ leadership capabilities
- Enhance personal thinking and decision-making
- Contribution to strategic control flexibility
- Enhance organizational competitiveness in the market place
- Instruments of change
- Increased executive time horizons.
- Better reporting system
- Improved mental model of business executive
- Help improve consensus building and communication
- Improve office automation
- Reduce time for finding information
- Early identification of company performance
- Detail examination of critical success factor
- Better understanding
- Time management
- Increased communication capacity and quality
Disadvantage of ESS
- Functions are limited
- Hard to quantify benefits
- Executive may encounter information overload
- System may become slow
- Difficult to keep current data
- May lead to less reliable and insecure data
Excessive cost for small company

0 Comments