Hidden Surface Removal
- One of the most challenging problems in computer graphics is the removal of hidden parts from images of solid objects.
- In real life, the opaque material of these objects obstructs the light rays from hidden parts and prevents us from seeing them.
- In the computer generation, no such automatic elimination takes place when objects are projected onto the screen coordinate system.
- Instead, all parts of every object, including many parts that should be invisible are displayed.
- To remove these parts to create a more realistic image, we must apply a hidden line or hidden surface algorithm to set of objects.
- The algorithm operates on different kinds of scene models, generate various forms of output or cater to images of different complexities.
- All use some form of geometric sorting to distinguish visible parts of objects from those that are hidden.
- Just as alphabetical sorting is used to differentiate words near the beginning of the alphabet from those near the ends.
- Geometric sorting locates objects that lie near the observer and are therefore visible.
- Hidden line and Hidden surface algorithms capitalize on various forms of coherence to reduce the computing required to generate an image.
- Different types of coherence are related to different forms of order or regularity in the image.
- Scan line coherence arises because the display of a scan line in a raster image is usually very similar to the display of the preceding scan line.
- Frame coherence in a sequence of images designed to show motion recognizes that successive frames are very similar.
- Object coherence results from relationships between different objects or between separate parts of the same objects.
- A hidden surface algorithm is generally designed to exploit one or more of these coherence properties to increase efficiency.
- Hidden surface algorithm bears a strong resemblance to two-dimensional scan conversions.
Types of hidden surface detection algorithms
- Object space methods
- Image space methods
Object space methods:
In this method, various parts of objects are compared. After comparison visible, invisible or hardly visible surface is determined. These methods generally decide visible surface. In the wireframe model, these are used to determine a visible line. So these algorithms are line based instead of surface based. Method proceeds by determination of parts of an object whose view is obstructed by other object and draws these parts in the same color.
Image space methods:
Here positions of various pixels are determined. It is used to locate the visible surface instead of a visible line. Each point is detected for its visibility. If a point is visible, then the pixel is on, otherwise off. So the object close to the viewer that is pierced by a projector through a pixel is determined. That pixel is drawn is appropriate color. These methods are also called a Visible Surface Determination. The implementation of these methods on a computer requires a lot of processing time and processing power of the computer.
The image space method requires more computations. Each object is defined clearly. Visibility of each object surface is also determined.
Differentiate between Object space and Image space method
| Object Space | Image Space |
|---|---|
| 1. Image space is object based. It concentrates on geometrical relation among objects in the scene. | 1. It is a pixel-based method. It is concerned with the final image, what is visible within each raster pixel. |
| 2. Here surface visibility is determined. | 2. Here line visibility or point visibility is determined. |
| 3. It is performed at the precision with which each object is defined, No resolution is considered. | 3. It is performed using the resolution of the display device. |
| 4. Calculations are not based on the resolution of the display so change of object can be easily adjusted. | 4. Calculations are resolution base, so the change is difficult to adjust. |
| 5. These were developed for vector graphics system. | 5. These are developed for raster devices. |
| 6. Object-based algorithms operate on continuous object data. | 6. These operate on object data. |
| 7. Vector display used for object method has large address space. | 7. Raster systems used for image space methods have limited address space. |
| 8. Object precision is used for application where speed is required. | 8. There are suitable for application where accuracy is required. |
| 9. It requires a lot of calculations if the image is to enlarge. | 9. Image can be enlarged without losing accuracy. |
| 10. If the number of objects in the scene increases, computation time also increases. | 10. In this method complexity increase with the complexity of visible parts. |
Similarity of object and Image space method
In both method sorting is used a depth comparison of individual lines, surfaces are objected to their distances from the view plane.
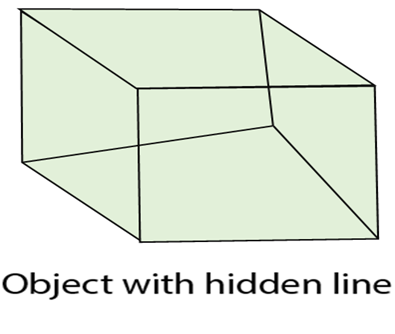
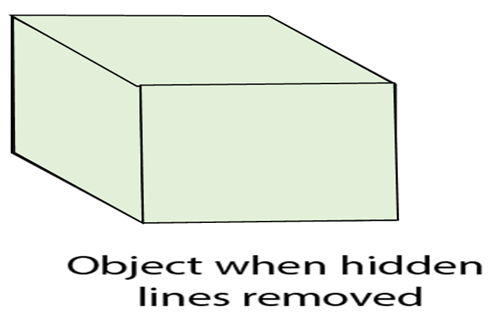
Considerations for selecting or designing hidden surface algorithms: Following three considerations are taken:
- Sorting
- Coherence
- Machine
Sorting: All surfaces are sorted in two classes, i.e., visible and invisible. Pixels are colored accordingly. Several sorting algorithms are available i.e.
- Bubble sort
- Shell sort
- Quick sort
- Tree sort
- Radix sort
Different sorting algorithms are applied to different hidden surface algorithms. Sorting of objects is done using x and y, z co-ordinates. Mostly z coordinate is used for sorting. The efficiency of sorting algorithm affects the hidden surface removal algorithm. For sorting complex scenes or hundreds of polygons complex sorts are used, i.e., quick sort, tree sort, radix sort. For simple objects selection, insertion, bubble sort is used.
Coherence
It is used to take advantage of the constant value of the surface of the scene. It is based on how much regularity exists in the scene. When we moved from one polygon of one object to another polygon of same object color and shearing will remain unchanged.
Types of Coherence
- Edge coherence
- Object coherence
- Face coherence
- Area coherence
- Depth coherence
- Scan line coherence
- Frame coherence
- Implied edge coherence
1. Edge coherence: The visibility of edge changes when it crosses another edge or it also penetrates a visible edge.
2. Object coherence: Each object is considered separate from others. In object, coherence comparison is done using an object instead of edge or vertex. If A object is farther from object B, then there is no need to compare edges and faces.
3. Face coherence: In this faces or polygons which are generally small compared with the size of the image.
4. Area coherence: It is used to group of pixels cover by same visible face.
5. Depth coherence: Location of various polygons has separated a basis of depth. Depth of surface at one point is calculated, the depth of points on rest of the surface can often be determined by a simple difference equation.
6. Scan line coherence: The object is scanned using one scan line then using the second scan line. The intercept of the first line.
7. Frame coherence: It is used for animated objects. It is used when there is little change in image from one frame to another.
8. Implied edge coherence: If a face penetrates in another, line of intersection can be determined from two points of intersection.
Algorithms used for hidden line surface detection
- Back Face Removal Algorithm
- Z-Buffer Algorithm
- Painter Algorithm
- Scan Line Algorithm
- Subdivision Algorithm
- Floating horizon Algorithm
3D Modelling System
It is a 2D modeling system plus the addition of some more extra primitives. 3D system includes all types of user-defined systems. The standard coordinate system used is called a world coordinate system. Whereas the user-defined coordinate system is called a user coordinate system.
It is of three types
-
- Solid Modelling System
- Solid Modelling System
- Surface Modelling System
- Wireframe Models
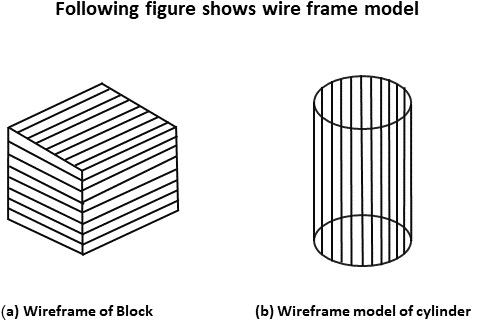
Wireframe Models: It has a lot of other names also i.e.
- Edge vertex models
- Stick figure model
- Polygonal net
- Polygonal mesh
- Visible line detection method
Wireframe model consists of vertex, edge (line) and polygons. Edge is used to join vertex. Polygon is a combination of edges and vertices. The edges can be straight or curved. This model is used to define computer models of parts, especially for computer-assisted drafting systems. Wireframe models are Skelton of lines. Each line has two endpoints. The visibility or appearance or look of the surface can be should using wireframe. If any hidden section exists that will be removed or represented using dashed lines. For determining hidden surface, hidden lines methods or visible line methods are used.
Advantage
- It is simple and easy to create.
- It requires little computer time for creation.
- It requires a short computer memory, so the cost is reduced.
- Wireframe provides accurate information about deficiencies of the surface.
- It is suitable for engineering models composed of straight lines.
- The clipping process in the wireframe model is also easy.
- For realistic models having curved objects, roundness, smoothness is achieved.
Disadvantage
- It is given only information about the outlook if do not give any information about the complex part.
- Due to the use of lines, the shape of the object lost in cluttering of lines.
- Each straight line will be represented as collections of four fold lines using data points. So complexity will be increased.
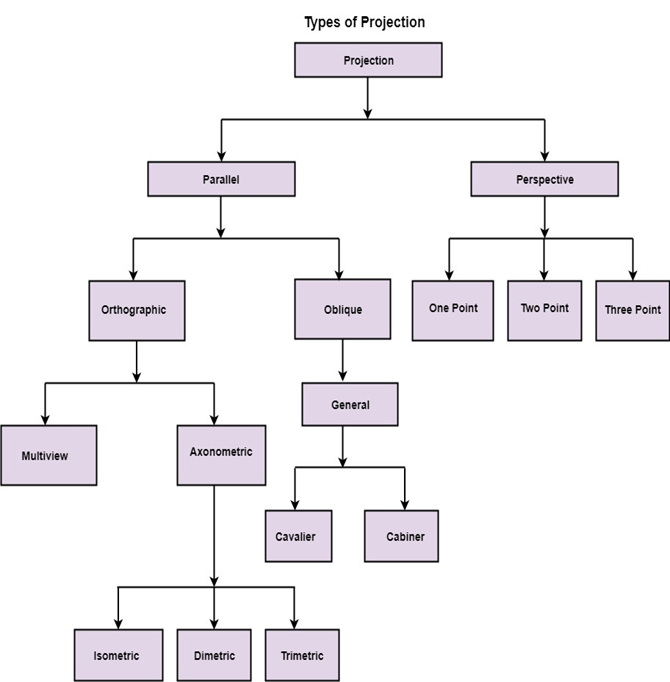
Projection
It is the process of converting a 3D object into a 2D object. It is also defined as mapping or transformation of the object in projection plane or view plane. The view plane is displayed surface.

0 Comments