Pointing and Positioning Techniques
Pointing technique refers to look at the items already on the screen whereas the positioning technique refers to position the item on the screen to a new position, i.e., the old current position. The user indicates a position on the screen with an input device, and this position is used to insert a symbol.
There are various pointing and positioning devices which are discussed below:
- Light Pen
- Mouse
- Tablet
- Joystick
- Trackball and spaceball
1. Light Pen:
It is a pointing device. When light pen is pointed at an item on the screen, it generates information from which the item can be identified by the program. It does not have any associated tracking hardware instead tracking is performed by software, making use of the output function of the display. All light pen programs depend on a rapid response from the pen when it is pointed at the screen fast response light pens can be build by using a highly sensitive photocell such as a photomultiplier tube.
2. Mouse:
It is a positioning device which consists of a small plastic box resting on two metal wheels whose axes are at right angles. Each wheel of the mouse is linked to a shaft encoder that delivers an electrical pulse for every incremental rotation of the wheel. As the mouse is rolled around on a flat surface, its movement in two orthogonal directions is translated into rotation of the wheels. These rotations can be measured by counting the pulses received from the shaft encoders. The connected values may be held in registers accessible to the computer on written directly into the computer memory. It is simple and low cost, and there is no need to pick it up to use it. The mouse sits on the table surface. But the mouse cannot be used for tracing data from paper since a small rotation of the mouse will cause an error in all the reading and it is complicated handprint character for recognition by the computer.
3. Tablet: It is also a positioning device and is used to describe a flat surface separate from the display, on which the user draws with a stylus. There are two types of tablets:
- Acoustic Tablet:
It depends on the use of strip microphones which are mounted along two adjacent edges of the tablet. The styles have a small piece of ceramic mounted close to its tip, and at regular intervals, a small spark is generated across the surface of the ceramic between two electrodes. The microphones pick up the pulse of sound produced by the spark and two counters record the delay between creating the spark and receiving the sound. These two delays are proportional to the stylus distance from the two edges of the tablet where the microphones are mounted.
- Electro-acoustic Tablet:
In this technique, the writing surface is a sheet of magneto strictive material acting as a row of delay lines. An electric pulse travels through the sheet first horizontally and then vertically and is detected by a sensor in the stylus. A counter is used to determine the delay from the time the pulse is issued to the time it is detected; from this value, the position of the stylus can be determined. The electro-acoustic tablet is quieter in operation than its acoustic counterpart and is less affected by noise or air movement.
4. Joystick:
A joystick consists of a small that is used to steer the screen cursor around. The distance that the stick is moved in any direction from its center position corresponds to the screen-cursor movement in that direction. Pressure sensitive joysticks have a non-moveable stick. Pressure on the stick is measured with strain gauges and converted to the movement of the cursor in the direction specified.
5. Trackball and spaceball:
Trackball is a ball that can be rotated with the fingers to produces screen-cursor movement potentiometers, attached to the ball, measure the amount and direction of rotation. Trackballs are after mounted on keyboards, whereas space-ball provides six degrees of freedom. Spaceballs is used for three-dimensional positioning and selection operation in virtual reality system, modeling, animation, CAD and other applications.
Elastic or Rubber Band Techniques
- Rubber banding is a popular technique of drawing geometric primitives such as line, polylines, rectangle, circle and ellipse on the computer screen.
- It becomes an integral part and de facto standard with the graphical user interface (GUI) for drawing and is almost universally accepted by all windows based applications.
- The user specifies the line in the usual way by positioning its two endpoints. As we move from the first endpoint to the second, the program displays a line from the first endpoint to the cursor position, thus he can see the lie of the line before he finishes positioning it.
- The effect is of an elastic line stretched between the first endpoint and the cursor; hence the name for these techniques.
Consider the different linear structures in fig (a) and fig (d), depending on the position of the cross-hair cursor. The user may move the cursor to generate more possibilities and select the one which suits him for a specific application.
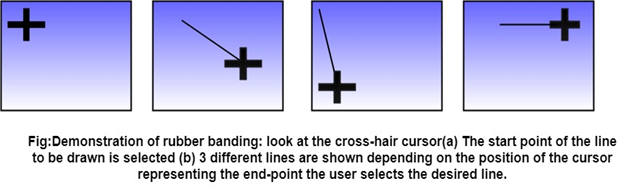
Selection of Terminal Point of the Line:
- The user moves the cursor to the appropriate position and selects.
- Then, as the cursor is moved, the line changes taking the latest positions of the cursors as the end-point.
- As long as the button is held down, the state of the rubber band is active.
The process is explained with the state transition diagram of rubber banding in fig:
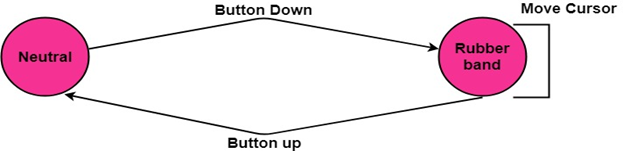
When the user is happy with the final position, the pressed button is released, and the line is drawn between the start and the last position of the cursor.
Example: This is widely followed in MS-Window based Applications like in the case of a paintbrush drawing package.
Other geometric entities can be drawn in a rubber-band fashion:
- Horizontally or vertically constructed lines
- Rectangles
- Arcs of circles
This technique is very helpful in drawing relatively complex entities such as rectangles and arcs.
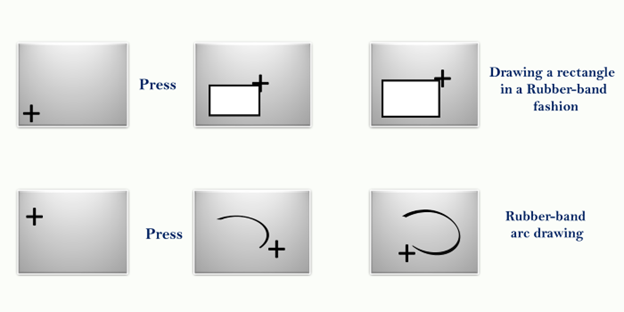
Advantage:
- It is used for drawing all geometric entities such as line, polygon, circle, rectangle, ellipse, and other curves.
- It is easy to understand and implement.
Disadvantage:
- It requires computational resources like software and CPU speed.
- Expensive
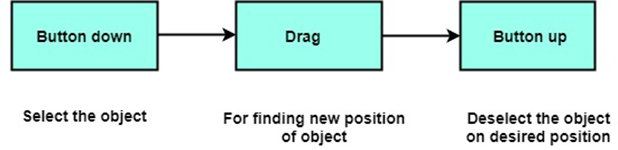
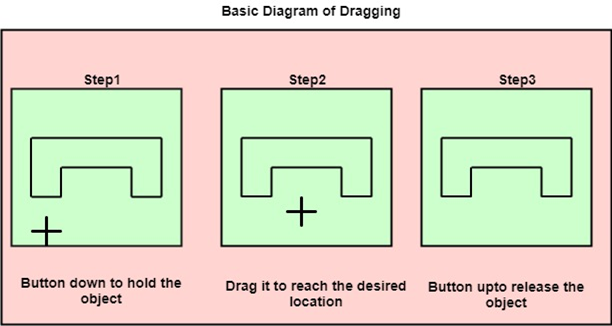
Dragging
Dragging is used to move an object from one position to another position on the computer screen. To drag any other object, first, we have to select the object that we want to move on the screen by holding the mouse button down. As cursor moved on the screen, the object is also moved with the cursor position. When the cursor reached the desired position, the button is released.
The following diagram represents the dragging procedure:
Animation
Animation refers to the movement on the screen of the display device created by displaying a sequence of still images. Animation is the technique of designing, drawing, making layouts and preparation of photographic series which are integrated into the multimedia and gaming products. Animation connects the exploitation and management of still images to generate the illusion of movement. A person who creates animations is called animator. He/she use various computer technologies to capture the pictures and then to animate these in the desired sequence. Animation includes all the visual changes on the screen of display devices. These are:
1. Change of shape as smile, sad and angry etc emoticon.
2. Change in size as very small circle, larger circle and biggest circle etc.
3. Change in color select red unselect white.
4. Change in structure as rotate a triangle.
5. Change in angle as counter clockwise and antilock wise:
Application Areas of Animation
1. Education and Training:
Animation is used in school, colleges and training centers for education purpose. Flight simulators for aircraft are also animation based.
2. Entertainment:
Animation methods are now commonly used in making motion pictures, music videos and television shows, etc.
3. Computer Aided Design (CAD):
One of the best applications of computer animation is Computer Aided Design and is generally referred to as CAD. One of the earlier applications of CAD was automobile designing. But now almost all types of designing are done by using CAD application, and without animation, all these work can’t be possible.
4. Advertising:
This is one of the significant applications of computer animation. The most important advantage of an animated advertisement is that it takes very less space and capture people attention.
5. Presentation:
Animated Presentation is the most effective way to represent an idea. It is used to describe financial, statistical, mathematical, scientific & economic data.
Animation Functions
1. Morphing:
Morphing is an animation function which is used to transform object shape from one form to another is called Morphing. It is one of the most complicated transformations. This function is commonly used in movies, cartoons, advertisement, and computer games. Example: Face App make one younger image into older.
The process of Morphing involves three steps:
- In the first step, one initial image and other final image are added to morphing application as shown in fig: Ist & 4th object consider as key frames.
- The second step involves the selection of key points on both the images for a smooth transition between two images as shown in 2nd object.
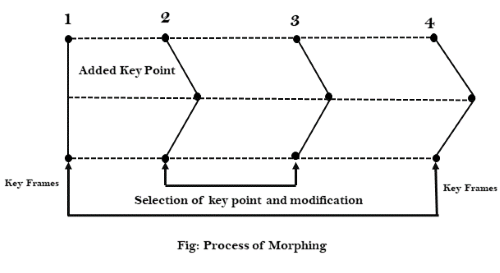
3. In the third step, the key point of the first image transforms to a corresponding key point of the second image as shown in 3rd object of the figure.
2. Wrapping:
Wrapping function is similar to morphing function. It distorts only the initial images so that it matches with final images and no fade occurs in this function.
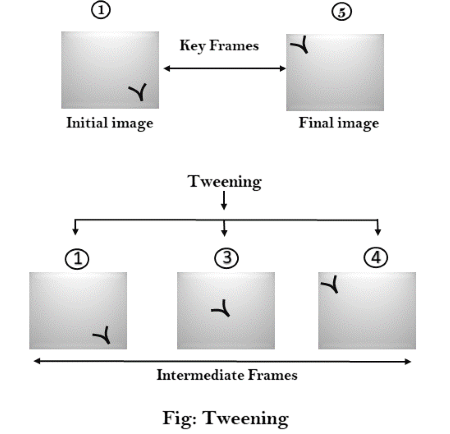
3. Tweening:
Tweening is the short form of ‘inbetweening.’ Tweening is the process of generating intermediate frames between the initial & last final images. This function is popular in the film industry.
4. Panning:
Usually Panning refers to rotation of the camera in horizontal Plane. In computer graphics, Panning relates to the movement of fixed size window across the window object in a scene. In which direction the fixed sized window moves, the object appears to move in the opposite direction as human walk but the moon in fix plane but seem to us moving with us. Another example running car and rain.
If the window moves in a backward direction, then the object appear to move in the forward direction and the window moves in forward direction then the object appear to move in a backward direction.
5. Zooming:
In zooming, the window is fixed an object and change its size, the object also appear to change in size. When the window is made smaller about a fixed center, the object comes inside the window appear more enlarged. This feature is known as Zooming In.
When we increase the size of the window about the fixed center, the object comes inside the window appear small. This feature is known as Zooming Out.
6. Fractals:
Fractal Function is used to generate a complex picture by using Iteration. Iteration means the repetition of a single formula again & again with slightly different value based on the previous iteration result. These results are displayed on the screen in the form of the display picture.

0 Comments