Filled Area Primitives:
Region filling is the process of filling image or region. Filling can be of boundary or interior region as shown in fig. Boundary Fill algorithms are used to fill the boundary and flood-fill algorithm are used to fill the interior.
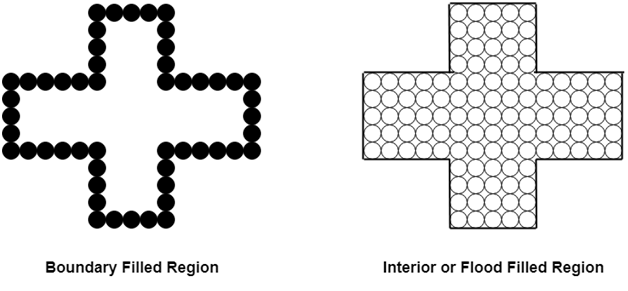
Boundary Filled Algorithm:
This algorithm uses the recursive method. First of all, a starting pixel called as the seed is considered. The algorithm checks boundary pixel or adjacent pixels are colored or not. If the adjacent pixel is already filled or colored then leave it, otherwise fill it.
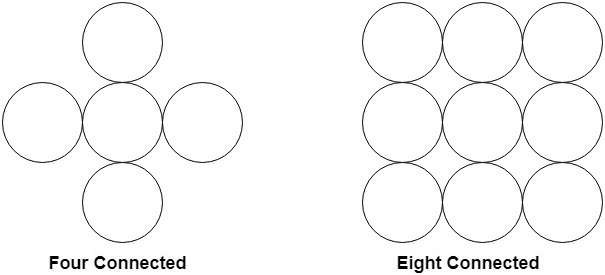
The filling is done using four connected or eight connected approaches.
Boundary Filled Algorithm
Four connected approaches is more suitable than the eight connected approaches.
1. Four connected approaches: In this approach, left, right, above, below pixels are tested.
2. Eight connected approaches: In this approach, left, right, above, below and four diagonals are selected.
Boundary can be checked by seeing pixels from left and right first. Then pixels are checked by seeing pixels from top to bottom. The algorithm takes time and memory because some recursive calls are needed.
Problem with recursive boundary fill algorithm:
It may not fill regions sometimes correctly when some interior pixel is already filled with color. The algorithm will check this boundary pixel for filling and will found already filled so recursive process will terminate. This may vary because of another interior pixel unfilled.
So check all pixels color before applying the algorithm.
Algorithm:
Procedure fill (x, y, color, color1: integer)
int c;
c=getpixel (x, y);
if (c!=color) (c!=color1)
{
setpixel (x, y, color)
fill (x+1, y, color, color 1);
fill (x-1, y, color, color 1);
fill (x, y+1, color, color 1);
fill (x, y-1, color, color 1);
}
Flood Fill Algorithm:
In this method, a point or seed which is inside region is selected. This point is called a seed point. Then four connected approaches or eight connected approaches is used to fill with specified color.
The flood fill algorithm has many characters similar to boundary fill. But this method is more suitable for filling multiple colors boundary. When boundary is of many colors and interior is to be filled with one color we use this algorithm.
In fill algorithm, we start from a specified interior point (x, y) and reassign all pixel values are currently set to a given interior color with the desired color. Using either a 4-connected or 8-connected approaches, we then step through pixel positions until all interior points have been repainted.
Disadvantage:
- Very slow algorithm
- May be fail for large polygons
- Initial pixel required more knowledge about surrounding pixels.
Algorithm:
-
Procedure floodfill (x, y,fill_ color, old_color: integer) If (getpixel (x, y)=old_color) { setpixel (x, y, fill_color); fill (x+1, y, fill_color, old_color); fill (x-1, y, fill_color, old_color); fill (x, y+1, fill_color, old_color); fill (x, y-1, fill_color, old_color); } }
Program1: To implement 4-connected flood fill algorithm:
-
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<graphics.h> #include<dos.h> void flood(int,int,int,int); void main() { intgd=DETECT,gm; initgraph(&gd,&gm,"C:/TURBOC3/bgi"); rectangle(50,50,250,250); flood(55,55,10,0); getch(); } void flood(intx,inty,intfillColor, intdefaultColor) { if(getpixel(x,y)==defaultColor) { delay(1); putpixel(x,y,fillColor); flood(x+1,y,fillColor,defaultColor); flood(x-1,y,fillColor,defaultColor); flood(x,y+1,fillColor,defaultColor); flood(x,y-1,fillColor,defaultColor); } }Output:
Program2: To implement 8-connected flood fill algorithm:
-
#include<stdio.h> #include<graphics.h> #include<dos.h> #include<conio.h> void floodfill(intx,inty,intold,intnewcol) { int current; current=getpixel(x,y); if(current==old) { delay(5); putpixel(x,y,newcol); floodfill(x+1,y,old,newcol); floodfill(x-1,y,old,newcol); floodfill(x,y+1,old,newcol); floodfill(x,y-1,old,newcol); floodfill(x+1,y+1,old,newcol); floodfill(x-1,y+1,old,newcol); floodfill(x+1,y-1,old,newcol); floodfill(x-1,y-1,old,newcol); } } void main() { intgd=DETECT,gm; initgraph(&gd,&gm,"C:\\TURBOC3\\BGI"); rectangle(50,50,150,150); floodfill(70,70,0,15); getch(); closegraph(); }
Output:

Scan Line Polygon Fill Algorithm:
This algorithm lines interior points of a polygon on the scan line and these points are done on or off according to requirement. The polygon is filled with various colors by coloring various pixels.
In above figure polygon and a line cutting polygon in shown. First of all, scanning is done. Scanning is done using raster scanning concept on display device. The beam starts scanning from the top left corner of the screen and goes toward the bottom right corner as the endpoint. The algorithms find points of intersection of the line with polygon while moving from left to right and top to bottom. The various points of intersection are stored in the frame buffer. The intensities of such points is keep high. Concept of coherence property is used. According to this property if a pixel is inside the polygon, then its next pixel will be inside the polygon.
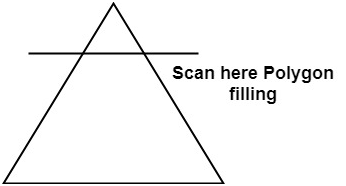
Side effects of Scan Conversion:
1. Staircase or Jagged: Staircase like appearance is seen while the scan was converting line or circle.
2. Unequal Intensity: It deals with unequal appearance of the brightness of different lines. An inclined line appears less bright as compared to the horizontal and vertical line.

0 Comments