Bresenham’s Circle Algorithm:
Scan-Converting a circle using Bresenham’s algorithm works as follows: Points are generated from 90° to 45°, moves will be made only in the +x & -y directions as shown in fig:
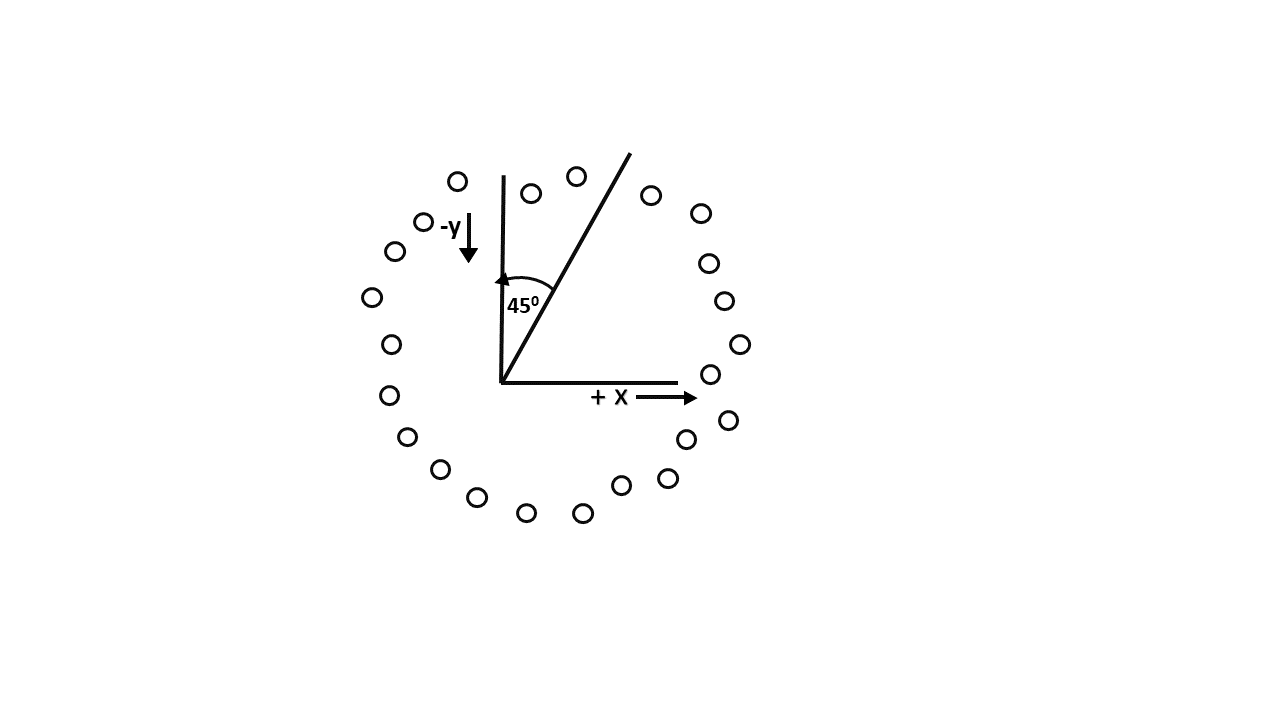
The best approximation of the true circle will be described by those pixels in the raster that falls the least distance from the true circle. We want to generate the points from
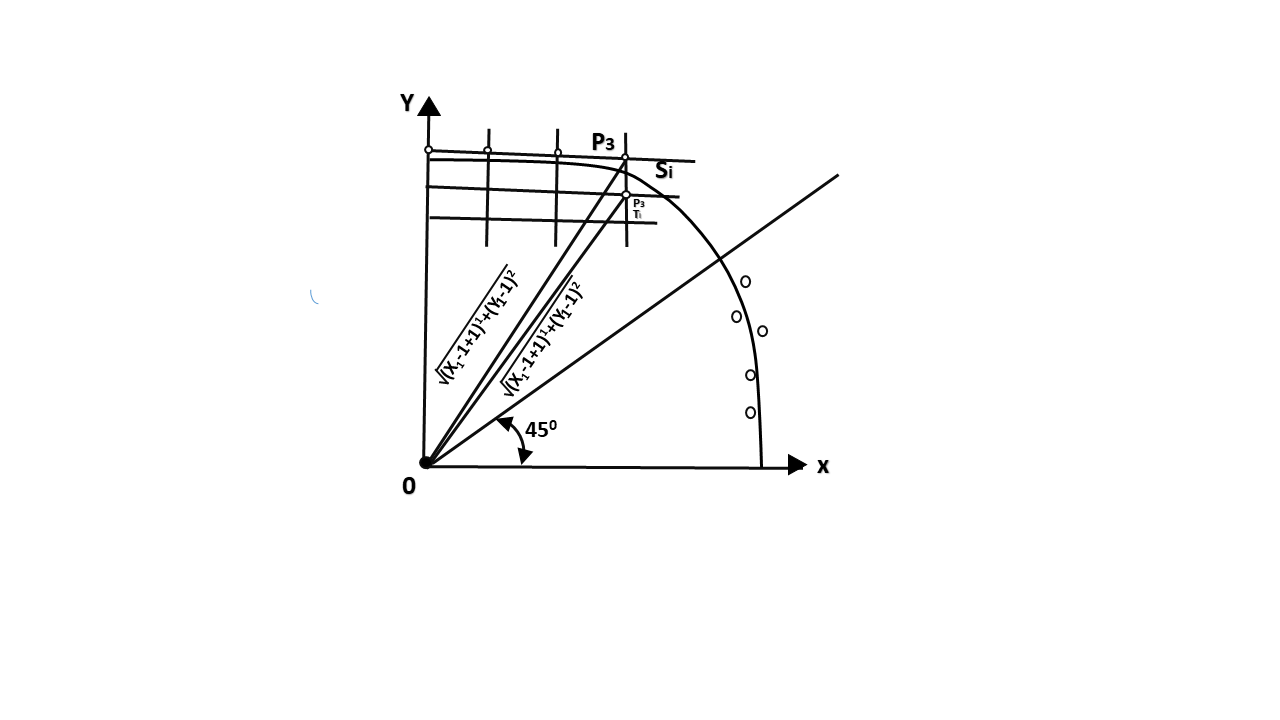
90° to 45°. Assume that the last scan-converted pixel is P1 as shown in fig. Each new point closest to the true circle can be found by taking either of two actions.
Move in the x-direction one unit or
Move in the x- direction one unit & move in the negative y-direction one unit.
Let D (Si) is the distance from the origin to the true circle squared minus the distance to point P3 squared. D (Ti) is the distance from the origin to the true circle squared minus the distance to point P2 squared. Therefore, the following expressions arise.
D (Si)=(xi-1+1)2+ yi-12 -r2
D (Ti)=(xi-1+1)2+(yi-1 -1)2-r2
Since D (Si) will always be +ve & D (Ti) will always be -ve, a decision variable d may be defined as follows:
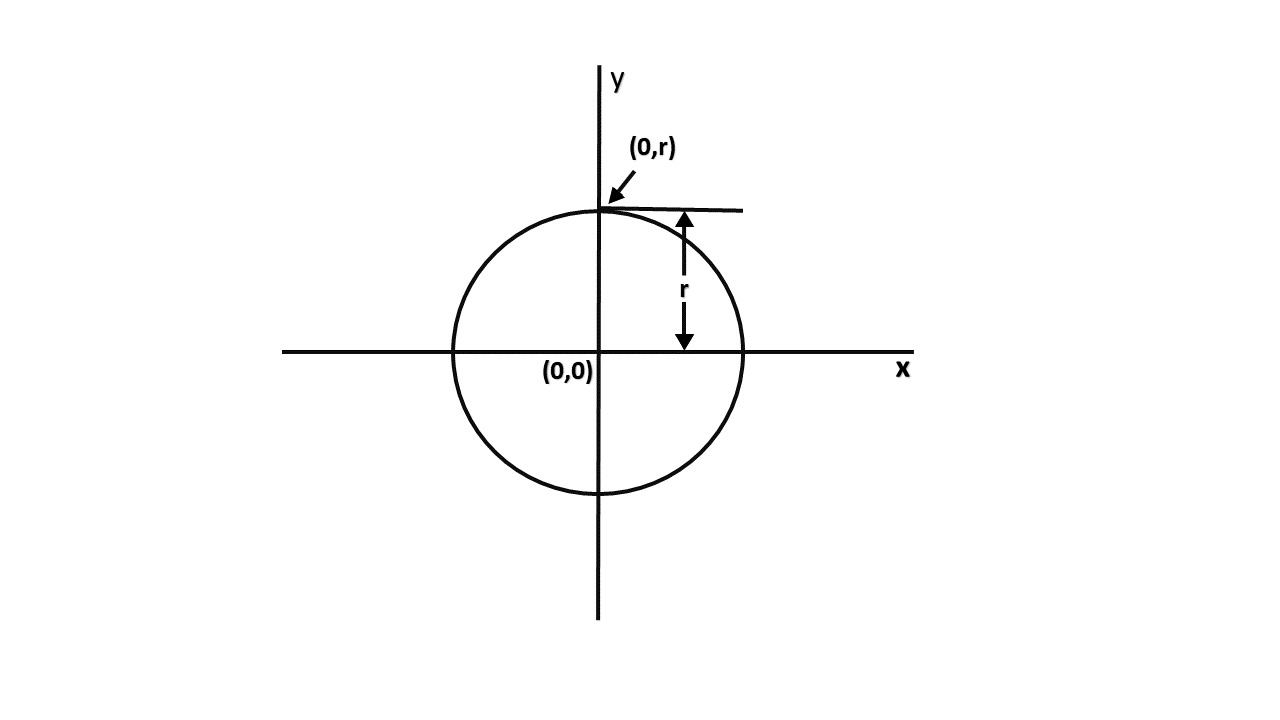
Bresenham’s Circle Algorithm
di=D (Si )+ D (Ti)
Therefore,
di=(xi-1+1)2+ yi-12 -r2+(xi-1+1)2+(yi-1 -1)2-r2
From this equation, we can drive initial values of di as
If it is assumed that the circle is centered at the origin, then at the first step x = 0 & y = r.
Therefore,
di=(0+1)2+r2 -r2+(0+1)2+(r-1)2-r2
=1+1+r2-2r+1-r2
= 3 – 2r
Thereafter, if d_i<0,then only x is incremented.
xi+1=xi+1 di+1=di+ 4xi+6
& if di≥0,then x & y are incremented
xi+1=xi+1 yi+1 =yi+ 1
di+1=di+ 4 (xi-yi)+10
Bresenham’s Circle Algorithm:
Step1: Start Algorithm
Step2: Declare p, q, x, y, r, d variables
p, q are coordinates of the center of the circle
r is the radius of the circle
Step3: Enter the value of r
Step4: Calculate d = 3 – 2r
Step5: Initialize x=0
&nbsy= r
Step6: Check if the whole circle is scan converted
If x > = y
Stop
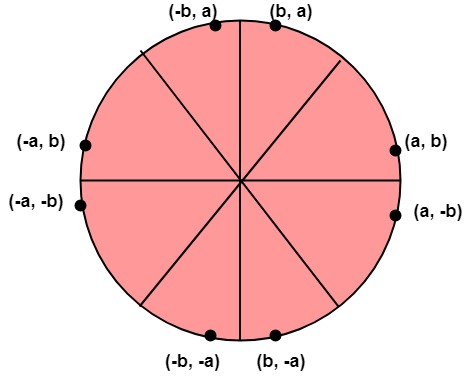
Step7: Plot eight points by using concepts of eight-way symmetry. The center is at (p, q). Current active pixel is (x, y).
putpixel (x+p, y+q)
putpixel (y+p, x+q)
putpixel (-y+p, x+q)
putpixel (-x+p, y+q)
putpixel (-x+p, -y+q)
putpixel (-y+p, -x+q)
putpixel (y+p, -x+q)
putpixel (x+p, -y-q)
Step8: Find location of next pixels to be scanned
If d < 0
then d = d + 4x + 6
increment x = x + 1
If d ≥ 0
then d = d + 4 (x – y) + 10
increment x = x + 1
decrement y = y – 1
Step9: Go to step 6
Step10: Stop Algorithm
Example: Plot 6 points of circle using Bresenham Algorithm. When radius of circle is 10 units. The circle has centre (50, 50).
Solution: Let r = 10 (Given)
Step1: Take initial point (0, 10)
d = 3 – 2r
d = 3 – 2 * 10 = -17
d < 0 ∴ d = d + 4x + 6
= -17 + 4 (0) + 6
= -11
Step2: Plot (1, 10)
d = d + 4x + 6 (∵ d < 0)
= -11 + 4 (1) + 6
= -1
Step3: Plot (2, 10)
d = d + 4x + 6 (∵ d < 0)
= -1 + 4 x 2 + 6
= 13
Step4: Plot (3, 9) d is > 0 so x = x + 1, y = y – 1
d = d + 4 (x-y) + 10 (∵ d > 0)
= 13 + 4 (3-9) + 10
= 13 + 4 (-6) + 10
= 23-24=-1
Step5: Plot (4, 9)
d = -1 + 4x + 6
= -1 + 4 (4) + 6
= 21
Step6: Plot (5, 8)
d = d + 4 (x-y) + 10 (∵ d > 0)
= 21 + 4 (5-8) + 10
= 21-12 + 10 = 19
So P1 (0,0)⟹(50,50)
P2 (1,10)⟹(51,60)
P3 (2,10)⟹(52,60)
P4 (3,9)⟹(53,59)
P5 (4,9)⟹(54,59)
P6 (5,8)⟹(55,58)
Program to draw a circle using Bresenham’s circle drawing algorithm:
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <math.h>
void EightWaySymmetricPlot(int xc,int yc,int x,int y)
{
putpixel(x+xc,y+yc,RED);
putpixel(x+xc,-y+yc,YELLOW);
putpixel(-x+xc,-y+yc,GREEN);
putpixel(-x+xc,y+yc,YELLOW);
putpixel(y+xc,x+yc,12);
putpixel(y+xc,-x+yc,14);
putpixel(-y+xc,-x+yc,15);
putpixel(-y+xc,x+yc,6);
}
void BresenhamCircle(int xc,int yc,int r)
{
int x=0,y=r,d=3-(2*r);
EightWaySymmetricPlot(xc,yc,x,y);
while(x<=y)
{
if(d<=0)
{
d=d+(4*x)+6;
}
else
{
d=d+(4*x)-(4*y)+10;
y=y-1;
}
x=x+1;
EightWaySymmetricPlot(xc,yc,x,y);
}
}
int main(void)
{
/* request auto detection */
int xc,yc,r,gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
/* initialize graphics and local variables */
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "C:\\TURBOC3\\BGI");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk) /* an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
printf("Enter the values of xc and yc :");
scanf("%d%d",&xc,&yc);
printf("Enter the value of radius :");
scanf("%d",&r);
BresenhamCircle(xc,yc,r);
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
Output:

MidPoint Circle Algorithm
It is based on the following function for testing the spatial relationship between the arbitrary point (x, y) and a circle of radius r centered at the origin:
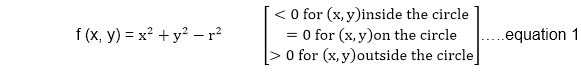
Now, consider the coordinates of the point halfway between pixel T and pixel S
This is called midpoint (xi+1,yi–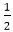 ) and we use it to define a decision parameter:
) and we use it to define a decision parameter:
Pi=f (xi+1,yi–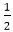 ) = (xi+1)2+(yi–
) = (xi+1)2+(yi–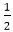 )2-r2 ……………equation 2
)2-r2 ……………equation 2
If Pi is -ve ⟹midpoint is inside the circle and we choose pixel T
If Pi is+ve ⟹midpoint is outside the circle (or on the circle)and we choose pixel S.
The decision parameter for the next step is:
Pi+1=(xi+1+1)2+(yi+1–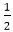 )2– r2…………equation 3
)2– r2…………equation 3
Since xi+1=xi+1, we have
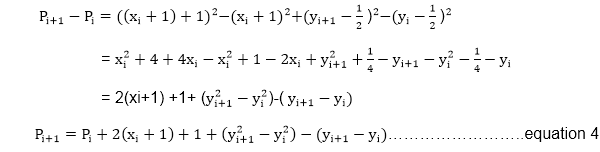
If pixel T is choosen ⟹Pi<0
We have yi+1=yi
If pixel S is choosen ⟹Pi≥0
We have yi+1=yi-1
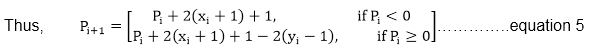
We can continue to simplify this in n terms of (xi,yi) and get
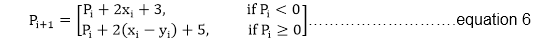
Now, initial value of Pi (0,r)from equation 2
MidPoint Circle Algorithm
We can put MidPoint Circle Algorithm≅1
∴r is an integer
So, P1=1-r
Algorithm:
Step1: Put x =0, y =r in equation 2
We have p=1-r
Step2: Repeat steps while x ≤ y
Plot (x, y)
If (p<0)
Then set p = p + 2x + 3
Else
p = p + 2(x-y)+5
y =y – 1 (end if)
x =x+1 (end loop)
Step3: End
Program to draw a circle using Midpoint Algorithm:
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <iostream.h>
class bresen
{
float x, y,a, b, r, p;
public:
void get ();
void cal ();
};
void main ()
{
bresen b;
b.get ();
b.cal ();
getch ();
}
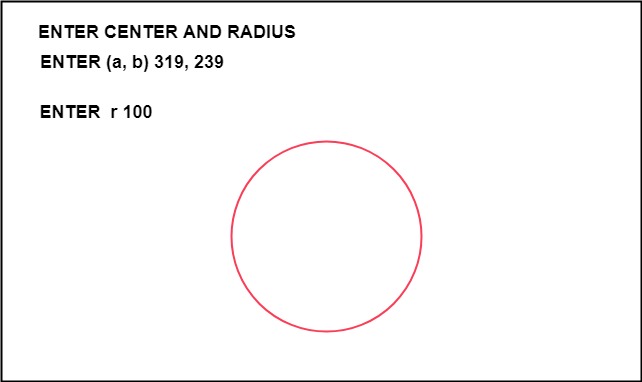
Void bresen :: get ()
{
cout<<"ENTER CENTER AND RADIUS";
cout<< "ENTER (a, b)";
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<"ENTER r";
cin>>r;
}
void bresen ::cal ()
{
/* request auto detection */
int gdriver = DETECT,gmode, errorcode;
int midx, midy, i;
/* initialize graphics and local variables */
initgraph (&gdriver, &gmode, " ");
/* read result of initialization */
errorcode = graphresult ();
if (errorcode ! = grOK) /*an error occurred */
{
printf("Graphics error: %s \n", grapherrormsg (errorcode);
printf ("Press any key to halt:");
getch ();
exit (1); /* terminate with an error code */
}
x=0;
y=r;
putpixel (a, b+r, RED);
putpixel (a, b-r, RED);
putpixel (a-r, b, RED);
putpixel (a+r, b, RED);
p=5/4)-r;
while (x<=y)
{
If (p<0)
p+= (4*x)+6;
else
{
p+=(2*(x-y))+5;
y--;
}
x++;
putpixel (a+x, b+y, RED);
putpixel (a-x, b+y, RED);
putpixel (a+x, b-y, RED);
putpixel (a+x, b-y, RED);
putpixel (a+x, b+y, RED);
putpixel (a+x, b-y, RED);
putpixel (a-x, b+y, RED);
putpixel (a-x, b-y, RED);
}
}
Output:

0 Comments