Defining a Circle:
Circle is an eight-way symmetric figure. The shape of circle is the same in all quadrants. In each quadrant, there are two octants. If the calculation of the point of one octant is done, then the other seven points can be calculated easily by using the concept of eight-way symmetry. For drawing, circle considers it at the origin. If a point is P1(x, y), then the other seven points will be
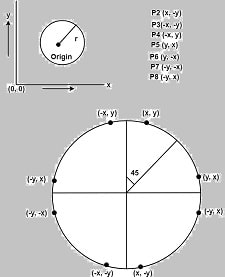
Defining a Circle
So we will calculate only 45°arc. From which the whole circle can be determined easily. If we want to display circle on screen then the putpixel function is used for eight points as shown below:
putpixel (x, y, color)
putpixel (x, -y, color)
putpixel (-x, y, color)
putpixel (-x, -y, color)
putpixel (y, x, color)
putpixel (y, -x, color)
putpixel (-y, x, color)
putpixel (-y, -x, color)
Example: Let we determine a point (2, 7) of the circle then other points will be (2, -7), (-2, -7), (-2, 7), (7, 2), (-7, 2), (-7, -2), (7, -2)
These seven points are calculated by using the property of reflection. The reflection is accomplished in the following way:
The reflection is accomplished by reversing x, y co-ordinates.
Defining a Circle
There are two standards methods of mathematically defining a circle centered at the origin.
- Defining a circle using Polynomial Method
- Defining a circle using Polar Co-ordinates
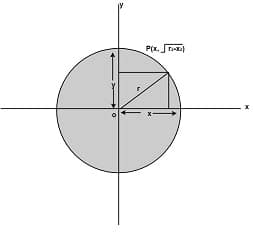
Defining a circle using Polynomial Method:
The first method defines a circle with the second-order polynomial equation as shown in fig:
y2=r2-x2
Where x = the x coordinate
y = the y coordinate
r = the circle radius
With the method, each x coordinate in the sector, from 90° to 45°, is found by stepping x from 0 to 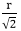 & each y coordinate is found by evaluating
& each y coordinate is found by evaluating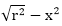 Defining a circle using Polynomial Method for each step of x.
Defining a circle using Polynomial Method for each step of x.
Defining a circle using Polynomial Method Algorithm:
Step1: Set the initial variables
r = circle radius
(h, k) = coordinates of circle center
x=o
I = step size
xend= Defining a circle using Polynomial Method
Step2: Test to determine whether the entire circle has been scan-converted.
If x > xend then stop.
Step3: Compute y = Defining a circle using Polynomial Method
Step4: Plot the eight points found by symmetry concerning the center (h, k) at the current (x, y) coordinates.
Plot (x + h, y +k) Plot (-x + h, -y + k)
Plot (y + h, x + k) Plot (-y + h, -x + k)
Plot (-y + h, x + k) Plot (y + h, -x + k)
Plot (-x + h, y + k) Plot (x + h, -y + k)
Step5: Increment x = x + i
Step6: Go to step (ii).
Program to draw a circle using Polynomial Method:
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
void setPixel(int x, int y, int h, int k)
{
putpixel(x+h, y+k, RED);
putpixel(x+h, -y+k, RED);
putpixel(-x+h, -y+k, RED);
putpixel(-x+h, y+k, RED);
putpixel(y+h, x+k, RED);
putpixel(y+h, -x+k, RED);
putpixel(-y+h, -x+k, RED);
putpixel(-y+h, x+k, RED);
}
main()
{
int gd=0, gm,h,k,r;
double x,y,x2;
h=200, k=200, r=100;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "C:\\TC\\BGI ");
setbkcolor(WHITE);
x=0,y=r;
x2 = r/sqrt(2);
while(x<=x2)
{
y = sqrt(r*r - x*x);
setPixel(floor(x), floor(y), h,k);
x += 1;
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
OUTPUT
Defining a circle using Polar Co-ordinates :
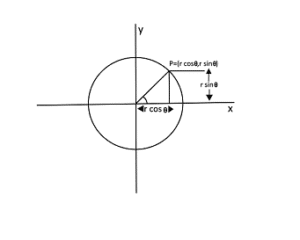
The second method of defining a circle makes use of polar coordinates as shown in fig:
x=r cos θ y = r sin θ
Where θ=current angle
r = circle radius
x = x coordinate
y = y coordinate
By this method, θ is stepped from 0 to Defining a circle using Polar Co-ordinates & each value of x & y is calculated.
Defining a circle using Polar Co-ordinates
Algorithm:
Step1: Set the initial variables:
r = circle radius
(h, k) = coordinates of the circle center
i = step size
θ_end=Defining a circle using Polar Co-ordinates
θ=0
Step2: If θ>θendthen stop.
Step3: Compute
x = r * cos θ y=r*sin?θ
Step4: Plot the eight points, found by symmetry i.e., the center (h, k), at the current (x, y) coordinates.
Plot (x + h, y +k) Plot (-x + h, -y + k)
Plot (y + h, x + k) Plot (-y + h, -x + k)
Plot (-y + h, x + k) Plot (y + h, -x + k)
Plot (-x + h, y + k) Plot (x + h, -y + k)
Step5: Increment θ=θ+i
Step6: Go to step (ii).
Program to draw a circle using Polar Coordinates:
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define color 10
using namespace std;
void eightWaySymmetricPlot(int xc,int yc,int x,int y)
{
putpixel(x+xc,y+yc,color);
putpixel(x+xc,-y+yc,color);
putpixel(-x+xc,-y+yc,color);
putpixel(-x+xc,y+yc,color);
putpixel(y+xc,x+yc,color);
putpixel(y+xc,-x+yc,color);
putpixel(-y+xc,-x+yc,color);
putpixel(-y+xc,x+yc,color);
}
void PolarCircle(int xc,int yc,int r)
{
int x,y,d;
x=0;
y=r;
d=3-2*r;
eightWaySymmetricPlot(xc,yc,x,y);
while(x<=y)
{
if(d<=0)
{
d=d+4*x+6;
}
else
{
d=d+4*x-4*y+10;
y=y-1;
}
x=x+1;
eightWaySymmetricPlot(xc,yc,x,y);
}
}
int main(void)
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int xc,yc,r;
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "c:\\turboc3\\bgi");
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
printf("Enter the values of xc and yc ,that is center points of circle : ");
scanf("%d%d",&xc,&yc);
printf("Enter the radius of circle : ");
scanf("%d",&r);
PolarCircle(xc,yc,r);
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
Output:

0 Comments