Programming with 8085
Let’s see some simple examples to demonstrate the use of some important instructions of 8085.
Problem: Write an assembly language program to add two 8 bit numbers stored at address 2050 and address 2051 in 8085 microprocessor. The starting address of the program is taken as 2000.
Example –
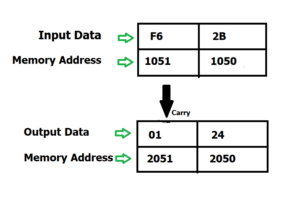
8085 instruction example
Algorithm :
- Load the first number from memory location 1050 to accumualator.
- Move the content of accumulator to register H.
- Load the second number from memory location 1051 to accumalator.
- Then add the content of register H and accumulator using “ADD” instruction and storing result at 2050
- The carry generated is recovered using “ADC” command and is stored at memory location 2051
Program:
| Memory Address | Mnemonics | Comment |
| 2000 | LDA 2050 | A<-[2050] |
| 2003 | MOV H, A | H<-A |
| 2004 | LDA 2051 | A<-[2051] |
| 2007 | ADD H | A<-A+H |
| 2008 | MOV L, A | L←A |
| 2009 | MVI A 00 | A←00 |
| 200B | ADC A | A←A+A+carry |
| 200C | MOV H, A | H←A |
| 200D | SHLD 3050 | H→3051, L→3050 |
| 2010 | HLT |
Explanation:
- LDA 1050 is used to moves the contents of 1050 memory location to the accumulator.
- MOV H, A is used to copies contents of Accumulator to register H to A
- LDA 1051 is used to moves the contents of 1051 memory location to the accumulator.
- ADD H is used to adds contents of A (Accumulator) and H register (F6). The result is stored in A itself. For all arithmetic instructions A is by default an operand and A stores the result as well
- MOV L, A is used to copies contents of A (24) to L
- MVI A 00 is used to moves immediate data (i.e., 00) to A
- ADC A adds contents of A(00), contents of register specified (for example: A) and carry (1). As ADC is also an arithmetic operation, A is by default an operand and A stores the result as well
- MOV H, A is used to copies contents of A (01) to H
- SHLD 2050 is used to moves the contents of L register (24) in 2050 memory location and contents of H register (01) in 2051 memory location
- HLT is used to stops executing the program and halts any further execution
The memory addresses given in the program are for a particular microprocessor kit. These addresses can be changed to suit the microprocessor kit available in your system.
Store 8-bit data in memory Program, Store 8-bit data in memory using direct addressing
MVI A, 49H : is used to Store 49H in the accumulator" STA 2501H : "Used to Copy accumulator contents at address 2501H" HLT : "Stop"
Store 8-bit data in memory using indirect addressing. Add two 8-bit numbers
LXI H : "is used to Load H-L pair with 2501H" MVI M : "is used to Store 49H in memory location pointed by H-L register pair (2501H)" HLT : "Stop"
Example
(2501 H) = 99H (2502 H) = 39H Result (2503 H) = 99H + 39H = D2H Since, 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 (99H) + 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 (39H) 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 (D2H)
Program
LXI H, 2501H : "Get address of first number in H-L pair. Now H-L points to 2501H" MOV A, M : "is used to Get first operand in accumulator" INX H : "is used to Increment content of H-L pair. Now, H-L points 2502H" ADD M : "is used to Add first and second operand" INX H : "is used to H-L points 4002H" MOV M, A : "is used to Store result at 2503H" HLT : "Stop"
Subtract two 8-bit numbers
Example
(2501 H) = 49H (2502 H) = 32H Result (2503 H) = 49H - 32H = 17H
Program
LXI H, 2501H : "is used to Get address of first number in H-L pair. Now H-L points to 2501H" MOV A, M : "is used to Get first operand in accumulator" INX H : "is used to Increment content of H-L pair. Now, H-L points 2502H" SUB M : "is used to Subtract first to second operand" INX H : "is used to H-L points 4002H" MOV M, A : "is used to Store result at 2503H" HLT : "Stop"
Add two 16-bits numbers
Add the 16-bit number in memory locations 2501H and 2502H to the 16-bit number in memory locations 2503H and 2504H. The most significant eight bits of the two numbers to be added are in memory locations 2502H and 4004H. Store the result in memory locations 2505H and 2506H with the most significant byte in memory location 2506H.
Example
(2501H) = 15H (2502H) = 1CH (2503H) = B7H (2504H) = 5AH Result = 1C15 + 5AB7H = 76CCH (2505H) = CCH (2506H) = 76H
Program
Add two 16-bits number with ADD and ADC instruction
LHLD 2501H : "is used to Get 1st 16-bit number in H-L pair" XCHG : "is used to Save 1st 16-bit number in DE" LHLD 2503H : "is used to Get 2nd 16-bit number in H-L pair" MOV A, E : "is used to Get lower byte of the 1st number" ADD L : "is used to Add lower byte of the 2nd number" MOV L, A : "is used to Store result in L-register" MOV A, D : "is used to Get higher byte of the 1st number" ADC H : "is used to Add higher byte of the 2nd number with CARRY" MOV H, A : "is used to Store result in H-register" SHLD 4004H : "is used to Store 16-bit result in memory locations 2505H and 2506H" HLT : "Stop"
Add two 16-bits numbers with DAD instruction
LHLD 2501H : "is used to Get 1st 16-bit number" XCHG : "is used to Save 1st 16-bit number in DE" LHLD 2503H : "is used to Get 2nd 16-bit number in H-L" DAD D : "is used to Add DE and HL" SHLD 2505H : "is used to Store 16-bit result in memory locations 2505H and 2506H". HLT : "Stop"
Subtract two 16-bit numbers
Example
(2500H) = 19H (2501H) = 6AH (2504H) = 15H (2503H) = 5CH Result = 6A19H ? 5C15H = OE04H (2504H) = 04H (2505H) = OEH
Program
LHLD 2500H : is used to Get first 16-bit number in HL XCHG : is used to Save first 16-bit number in DE" LHLD 2502H : is used to Get second 16-bit number in HL" MOV A, E : is used to Get lower byte of the first number" SUB L : is used to Subtract lower byte of the second number" MOV L, A : is used to Store the result in L register" MOV A, D : is used to Get higher byte of the first number" SBB H : is used to Subtract higher byte of second number with borrow" MOV H, A : is used to Store l6-bit result in memory locations 2504H and 2505H" SHLD 2504H : is used to Store l6-bit result in memory locations 2504H and 2505H" HLT : is used to Terminate program execution"
Add contents of two memory locations
Example
(2500H) = 7FH (2501H) = 89H Result = 7FH + 89H = lO8H (2502H) = 08H (2503H) = 01H
Program
LXI H, 2500H : "is used to HL Points 2500H" MOV A, M : "Get first operand" INX H : "HL Points 2501H" ADD M : "this statement Add second operand" INX H : "is used to HL Points 2502H" MOV M, A : "this statement Store the lower byte of result at 2502H" MVIA, 00 : "Initialize higher byte result with 00H" ADC A : "this statement Add carry in the high byte result" INX H : "is used to HL Points 2503H" MOV M, A : "this statement Store the higher byte of result at 2503H" HLT : "Terminate program execution"
Finding 1’s complement of a number
To obtain one’s complement of a number its 0 bits are replaced by 1 and 1 by 0.
Example 1
(2501H) = 96 H = 1001 0110 (9) (6) One's complement = 0110 1001 = 69 H Result = (2502H) = 69H
Example 2
(2501H) = E4H Result = (2502H) = 1BH
Program
The number is placed in the memory location 2501 H.
The result is stored in the memory location 2502 H.
LDA 2501H : "this statement Get the number IN accumulator" CMA : "this statement take its complement" STA 2502H : "this statement Store result in 2502H" HLT : "Stop"
Finding 2’s complement of a number
2’s complement of a number is obtained by adding 1 to the 1’s complement of the number.
Example
To find the two’s complement of 96.
96 = 1001 0110 1's complement = 0110 1001 = 69 + 0000 0001 2's complement = 0110 1010 = 6A
Program
The number is placed in the memory location 2501 H.
The result is to be stored in the memory location 2502 H.
LDA 2501 H : "this statement Get data in accumulator" CMA : "Take its 1's complement" ADI, 01 H : "this statement Add one in the number" STA 2502 H : "Store the result in 2502 H" HLT : "Stop"
Count number of 1’s in a number
Example
2501 H = 04 2502 H = 34 H 2503 H = A9H 2504 H = 78H 2505 H = 56H Result = 2503 H = A9H
Program
Count number of 1’s of the content of the register D and store the count in the register B.
MVI B, 00H MVI C, 08H MOV A, D BACK: RAR JNC SKIP INR B SKIP: DCR C JNZ BACK HLT
Find larger of two numbers
Example
2501H = 98 H 2502H = 87H Result = 98H (2503H)
Program
The first number 98H is placed in the memory location 2501 H. The second number 87H is placed in the memory location 2502H. The result is stored in the memory location 2503 H. LXI H, 2501H : "this statement Address of first number in H-L pair" MOV A, M : "1stt number in accumulator" INX H : "this statement Address of 2nd number in H-L pair" CMP M : "compare 2nd number with 1st number" JNC AHEAD : "No, larger is in accumulator. Go to AHEAD" MOV A, M : "this statement Yes, get 2nd number in the accumulator" STA 2503 H : "Store larger number in 2503H" HLT : "Stop"
Find smaller of two numbers
Example
2501H = 84 H 2502H = 99 H Result = 84 H(2503H)
Program
The first number 84H is placed in the memory location 2501 H.
The second number 99H is placed in the memory location 2502H.
The result is stored in the memory location 2503 H.
LXI H, 2501H : "Address of first number in H-L pair" MOV A, M : "this statement 1stt number in accumulator" INX H : "Address of 2nd number in H-L pair" CMP M : "compare 2nd number with 1st number" JC AHEAD : "this statement Yes, smaller number is in accumulator. Go to AHEAD" MOV A, M : "No, get 2nd number in the accumulator" STA 2503 H : "this statement Store smaller number in 2503H" HLT : "Stop"
Calculate the sum of series of even numbers
Example
2500 H = 4H 2501 H = 20H 2502 H = 15H 2503 H = 13H 2504 H = 22H Result = 2505 H = 20+22= 42H
Program
The numbers are placed in the memory locations 2501 to 2504H.
The sum is to be stored in the memory location 2450H.
As there are 4 numbers in the series, count = 04
The initial value of the sum is made 00. The even number of the series are taken one by one and added to the sum.
LDA 2500H MOV C, A : "Initialize counter" MVI B, 00H : "sum = 0" LXI H, 2501H :this statement Initialize pointer" BACK: MOV A, M : "Get the number" ANI 01H : "Mask Bit l to Bit7" JNZ SKIP : this statement Don't add if number is ODD" MOV A, B : this statement Get the sum" ADD M : "SUM = SUM + data" MOV B, A : "Store result in B register" SKIP: INX H : "increment pointer" DCR C : "Decrement counter" JNZ BACK : "if counter 0 repeat" STA 2505H : "store sum" HLT : "Stop"
Calculate the sum of series of odd numbers
Example
2500 H = 4H 2501 H = 9AH 2502 H = 52H 2503 H = 89H 2504 H = 3FH Result = 2505 H = 89H + 3FH= C8H
Program
The numbers are placed in the memory locations 2501 to 2504H.
The sum is to be stored in the memory location 2450H.
As there are 4 numbers in the series, count = 04
The initial value of the sum is made 00. The odd number of the series are taken one by one and added to the sum.
LDA 2500H MOV C, A : "Initialize counter" LXI H, 2501H : "Initialize pointer" MVI E, 00 : "Sum low = 0" MOV D, E : "Sum high = 0" BACK: MOV A, M : "Get the number" ANI 01H : "Mask Bit 1 to Bit-7" JZ SKIP : this statement Don't add if number is even" MOV A, E : "Get the lower byte of sum" ADD M : "Sum = sum + data" MOV E, A : this statement Store result in E register" JNC SKIP INR D : "Add carry to MSB of SUM" SKIP: INX H : "Increment pointer"
Find the square of given number
Program
Find the square of 07 (decimal) using lookup table techniques.
The number 07 D is in the memory.
The result is to be stored in the memory location 2501H.
The table for square is stored from 2600 to 2609 H.
LDA 2500H : "Get data in accumulator" MOV L, A : this statement Get data in register L" MVI H, 26H : "Get 26 in register H" MOV A, M : this statement Square of data in accumulator" STA 2501 H : "Store Square in 2501 H" HLT : "Stop"
Separate even numbers from given numbers
Program
A program to separate even numbers from the given list of 50 numbers and store them in other location starting from 2600H.
Starting location of 50 number list is 2500H.
LXI H, 2500H : "Initialize memory pointer 1" LXI D, 2600H : "Initialize memory pointer2" MVI C, 32H : "Initialize counter" BACK:MOV A, M : this statement Get the number" ANI 01H : "Check for even number" JNZ SKIP : "If ODD, don't store" MOV A, M : "Get the number" STAX D : this statement Store the number in result list" INX D : "Increment pointer 2" SKIP: INX H : "Increment pointer 1" DCR C : "Decrement counter" JNZ BACK : "If not zero, repeat" HLT : "Stop"

0 Comments