What is Spiral Model?
Spiral Model is a risk-driven software development process model with the amalgamation of waterfall model and iterative model. Spiral Model helps to implement software development elements of several process models for the software project based on unique risk patterns ensuring efficient development process.
Spiral model each phase in software engineering initiates with a design goal and ends with the client reviewing the progress. The development process in Spiral model in SDLC, starts with a small set of necessity and goes through each development phase for those set of requirements. The software engineering team enhances functionality for the additional requirement in every-increasing spirals until the application is ready for the production phase. The below figure very well explain Spiral Model:
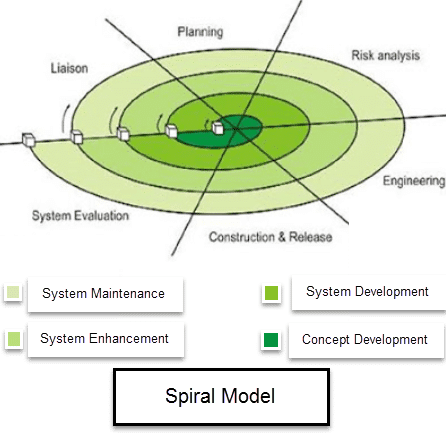
Spiral Model Phases
| Spiral Model Phases | Activities corresponding each phase |
| Planning | This phase includes guessing the cost, schedule and resources for the iteration. It also involves understanding the system requirements for continuous communication between the system analyst and the customer |
| Risk Analysis | Risk Analysis is the Identification of potential risk is done while risk mitigation strategy is planned and finalized |
| Engineering | The phase includes testing, coding and deploying software at the customer site |
| Evaluation | This phase concern Evaluation of software by the customer. Similarly, take account of identifying and monitoring risks such as schedule slippage and cost overrun |
Spiral Model Usage:
- Spiral methodology is useful for medium to high-risk projects
- When necessities are undecided and complex, Spiral model in SDLC is useful
- Where modifications may require at any time
- When risk and costs evaluation is important
- Where long term project commitment is not feasible due to changes in economic priorities
- For a large project spiral model in software engineering is used.
- When releases are required to be frequent, spiral methodology is used
- When creation of a prototype is applicable
- When there is a budget constraint and risk evaluation is important.
- For medium to high-risk projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Spiral Model
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| At a later stage Additional functionality or changes can be done. | Risk of not meeting the schedule or budget |
| Cost estimation becomes easy due to prototype building is done in small fragments | Spiral development works best for large projects only also demands risk assessment expertise |
| It is Continuous or repeated development helps in risk management | For its smooth operation spiral model protocol needs to be followed strictly |
| The Development is fast and features are added in a systematic way in Spiral development | In This model the Documentation is more as it has intermediate phases |
| There is always a space for customer feedback | Spiral software development is not advisable for smaller project, it might cost them a lot. |
| Changing requirements can be accommodated. | Management is more complex |
Users see the system early. | Spiral model process is complex. |
The risky parts can be developed earlier which helps in better risk management. | Spiral may go on indefinitely. Large number of intermediate stages requires excessive documentation. |

0 Comments