Post-order:
Post-order traverse need to traverse left, then right then root. Array, Linked List, Queues, Stacks, etc. are linear traversal where have only one logical way to traverse them. Though trees can be traversed in different ways. That Traversals:
For Post-order traverse need to traverse left, then right then root.
Following figure Post -Order traverse 2, 7, 9.
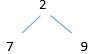
tree
Algorithm for Post-order traverse.
Input tree, root.
Step 1: Traverse left sub tree like call Pre-order (tree, root. left).
Step 2: Traverse right sub tree like call Pre-order (tree, root. right).
Step 3: visit root node.
Now, Traverse the following tree by following program.
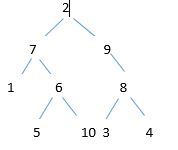
tree
Traverse : 1, 5, 10, 6, 7, 3, 4, 8, 9, 2.
Recent Articles on Binary Tree in the blog Topic :
- Introduction Of Binary Tree
- Traversals such as
- In-order traversal tree with C implementation
- Post-order traversal tree with C implementation
- Pre-order traversal tree with C implementation
Implementation Process for Post-order traverse:
- 1st need to create node struct where data, *left , *right declared;
- 2nd need to create new node function which take an item and return new node, where firstly need i) memory allocation same as datatype size. If failed to memory allocation show error or assign data into new node,if left or right child no value then put them as NULL.
- 3rd to add child left and right need two function both take two input one for node pointer another for left or right child assigned.
- 4th create create_tree() function by create_node ,add_left_child() and right_child() function. This function return root.
- 5th Now use post_order() recursion function, if left child not null call post_order() recursively for left node,Again if right child not null call post_order()recursively for right node, root print.
- 6th main() function receive root data or value will print.
Implementation Using C :
A
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct node Node;
struct node
{
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
Node *create_node (int item)
{
Node *new_node = (Node *) malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(new_node == NULL)
{
printf(“Error ! Could not create an Error\n”);
exit(1);
}
new_node -> data = item;
new_node -> left= NULL;
new_node ->right =NULL;
return (new_node);
}
void add_left_child( Node *node, Node *child )
{
node->left =child;
}
void add_right_child( Node *nodee, Node *child )
{
nodee->right =child;
}
Node *create_tree()
{
Node *two = create_node(2);
Node *seven=create_node(7);
Node *nine=create_node(9);
add_left_child(two,seven);
add_right_child(two,nine);
Node *one = create_node(1);
Node *six = create_node(6);
add_left_child(seven,one);
add_right_child(seven,six);
Node *five=create_node(5) ;
Node *ten = create_node(10);
add_left_child(six,five);
add_right_child(six,ten);
Node *eight = create_node(8);
add_right_child(nine,eight);
Node *three=create_node(3);
Node *four=create_node(4);
add_left_child(eight,three);
add_right_child(eight,four);
return two;
}
void post_order(Node *node)
{
if(node->left != NULL)
{
post_order(node->left);
}
if(node->right != NULL)
{
post_order(node->right);
}
printf(“%d “,node->data);
}
struct Node node;
int main()
{
Node *root =create_tree();
post_order(root);
printf(” “);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT: 1 5 10 6 7 3 4 8 9 2
Data Structure more articles
- PostOrder traverse C Program For Pre_Order traversal in a Tree.
- In order traverse C program In_order Traversal of a Tree.
- Post order traversal
Post-order traverse of a Tree with C program.

0 Comments