8086 pins configuration
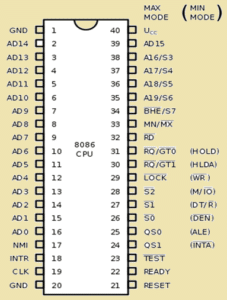
The description of the pins of 8086 is as follows:
Address Data Bus PIN in details:
AD0-AD15 (Address Data Bus): Bidirectional address/data lines. These are low order address bus. They are multiplexed with data. When these lines are used to transmit memory address, the symbol A is used instead of AD, for example, A0- A15.
A16 – A19 (Output): High order address lines. These are multiplexed with status signals.
A16/S3, A17/S4: A16 and A17 are multiplexed with segment identifier signals S3 and S4.
A18/S5: A18 is multiplexed with interrupt status S5.
A19/S6: A19 is multiplexed with status signal S6.
BHE/S7 (Output):
Bus High Enable/Status. During T1, it is low. It enables the data onto the most significant half of data bus, D8-D15. 8-bit device connected to upper half of the data bus use BHE signal. It is multiplexed with status signal S7. S7 signal is available during T3 and T4.
RD (Read):
For read operation. It is an output signal. It is active when LOW. Ready (Input): The addressed memory or I/O sends acknowledgment through this pin. When HIGH, it denotes that the peripheral is ready to transfer data.
RESET (Input): System reset. The signal is active HIGH.
CLK (input): Clock 5, 8 or 10 MHz
INTR: Interrupt Request.
NMI (Input): Non-maskable interrupt request.
TEST (Input): Wait for test control. When goes to LOW the microprocessor continues execution otherwise waits.
VCC: Power supply +5V dc.
GND: Ground.
Operating Modes of 8086
There are two operating modes of operation for Intel 8086, namely the minimum mode and the maximum mode. When only one 8086 CPU is to be used in a microprocessor system, the 8086 is used in the Minimum mode of operation. In a multiprocessor system 8086 operates in the Maximum mode.
Pin Description for Minimum Mode
In this minimum mode of operation, the pin MN/MX is connected to 5V D.C. supply i.e. MN/MX = VCC.
The description about the pins from 24 to 31 for the minimum mode is as follows:
INTA (Output):
Pin number 24 interrupts acknowledgement. On receiving interrupt signal, the processor issues an interrupt acknowledgment signal. It is active LOW.
ALE (Output):
Pin no. 25. Address latch enable. It goes HIGH during T1. The microprocessor 8086 sends this signal to latch the address into the Intel 8282/8283 latch.
DEN (Output):
Pin no. 26. Data Enable. When Intel 8287/8286 octal bus transceiver is used this signal. It is active LOW.
DT/R (output):
Pin No. 27 data Transmit/Receives. When Intel 8287/8286 octal bus transceiver is used this signal controls the direction of data flow through the transceiver. When it is HIGH, data is sent out. When it is LOW, data is received.
M/IO (Output):
Pin no. 28, Memory or I/O access. When this signal is HIGH, the CPU wants to access memory. When this signal is LOW, the CPU wants to access I/O device.
WR (Output): Pin no. 29, Write. When this signal is LOW, the CPU performs memory or I/O write operation.
HLDA (Output):
Pin no. 30, Hold Acknowledgment. It is sent by the processor when it receives HOLD signal. It is active HIGH signal. When HOLD is removed HLDA goes LOW.
HOLD (Input):
Pin no. 31, Hold. When another device in microcomputer system wants to use the address and data bus, it sends HOLD request to CPU through this pin. It is an active HIGH signal.
Pin Description for Maximum Mode
In the maximum mode of operation, the pin MN/¯MX is made LOW. It is grounded. The description about the pins from 24 to 31 is as follows:
QS1, QS0 (Output): Pin numbers 24, 25, Instruction Queue Status. Logics are given below:
| QS1 | QS0 | Operation |
| 0 | 0 | No operation |
| 0 | 1 | 1st byte of opcode from queue. |
| 1 | 0 | Empty the queue |
| 1 | 1 | Subsequent byte from queue |
S0, S1, S2 (Output):
Pin numbers 26, 27, 28 Status Signals. These signals are connected to the bus controller of Intel 8288. This bus controller generates memory and I/O access control signals. Logics for status signal are given below:
| S2 | S1 | S0 | Operation |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | Interrupt acknowledgement |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Read data from I/O port |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Write data from I/O port |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | Halt |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Opcode fetch |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Memory read |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Memory write |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Passive state |
LOCK (Output):
Pin no. 29. It is an active LOW signal. When this signal is LOW, all interrupts are masked and no HOLD request is granted. In a multiprocessor system all other processors are informed through this signal that they should not ask the CPU for relinquishing the bus control.
RG/GT1, RQ/GT0 (Bidirectional):
Pin numbers 30, 31, Local Bus Priority Control. Other processors ask the CPU by these lines to release the local bus. In the maximum mode of operation signals WR, ALE, DEN, DT/R etc. are not available directly from the processor. These signals are available from the controller 8288.
The 8086 microprocessor supports 8 types of instructions
- Data Transfer Instructions
- Arithmetic Instructions
- Bit Manipulation Instructions
- String Instructions
- Program Execution Transfer Instructions (Branch & Loop Instructions)
- Processor Control Instructions
- Iteration Control Instructions
- Interrupt Instructions
Data Transfer Instructions:
These instructions are used to transfer the data from the source operand to the destination operand. Following are the list of instructions under this group:
Instruction to transfer a word
MOV: Used to copy the byte or word from the provided source to the provided destination.
PPUSH: Used to put a word at the top of the stack.
POP: Used to get a word from the top of the stack to the provided location.
PUSHA: Used to put all the registers into the stack.
POPA: Used to get words from the stack to all registers.
XCHG: Used to exchange the data from two locations.
XLAT: Used to translate a byte in AL using a table in the memory.
Instructions for input and output port transfer
IN: Used to read a byte or word from the provided port to the accumulator.
OUT: Used to send out a byte or word from the accumulator to the provided port.
Instructions to transfer the address
LEA: Used to load the address of operand into the provided register.
LDS: Used to load DS register and other provided register from the memory
LES: Used to load ES register and other provided register from the memory.
Instructions to transfer flag registers
LAHF: Used to load AH with the low byte of the flag register.
SAHF: Used to store AH register to low byte of the flag register.
PUSHF : Used to copy the flag register at the top of the stack.
POPF: Used to copy a word at the top of the stack to the flag register.
Arithmetic Instructions
These instructions are used to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc. Following is the list of instructions under this group:
Instructions to perform addition
- ADD: Used to add the provided byte to byte/word to word.
- ADC: Used to add with carry.
- INC: Used to increment the provided byte/word by 1.
- AAA: Used to adjust ASCII after addition.
- DAA: Used to adjust the decimal after the addition/subtraction operation.
Instructions to perform subtraction
- SUB: Used to subtract the byte from byte/word from word.
- SBB: Used to perform subtraction with borrow.
- DEC: Used to decrement the provided byte/word by 1.
- NPG: Used to negate each bit of the provided byte/word and add 1/2’s complement.
- CMP: Used to compare 2 provided byte/word.
- AAS: Used to adjust ASCII codes after subtraction.
- DAS: Used to adjust decimal after subtraction.
Instruction to perform multiplication
- MUL : Used to multiply unsigned byte by byte/word by word.
- IMUL: Used to multiply signed byte by byte/word by word.
- AAM: Used to adjust ASCII codes after multiplication.
Instructions to perform division
DIV − Used to divide the unsigned word by byte or unsigned double word by word.
- IDIV − Used to divide the signed word by byte or signed double word by word.
- AAD − Used to adjust ASCII codes after division.
- CBW − Used to fill the upper byte of the word with the copies of sign bit of the lower byte.
- CWD − Used to fill the upper word of the double word with the sign bit of the lower word.
Bit Manipulation Instructions
These instructions are used to perform operations where data bits are involved, i.e. operations like logical, shift, etc.
Following is the list of instructions under this group:
Instructions to perform logical operation
- NOT − Used to invert each bit of a byte or word.
- AND − Used for adding each bit in a byte/word with the corresponding bit in another byte/word.
- OR − Used to multiply each bit in a byte/word with the corresponding bit in another byte/word.
- XOR − Used to perform Exclusive-OR operation over each bit in a byte/word with the corresponding bit in another byte/word.
- TEST − Used to add operands to update flags, without affecting operands.
Instructions to perform shift operations
- SHL/SAL − Used to shift bits of a byte/word towards left and put zero(S) in LSBs.
- SHR − Used to shift bits of a byte/word towards the right and put zero(S) in MSBs.
- SAR − Used to shift bits of a byte/word towards the right and copy the old MSB into the new MSB.
Instructions to perform rotate operations
- ROL − Used to rotate bits of byte/word towards the left, i.e. MSB to LSB and to Carry Flag [CF].
- ROR − Used to rotate bits of byte/word towards the right, i.e. LSB to MSB and to Carry Flag [CF].
- RCR − Used to rotate bits of byte/word towards the right, i.e. LSB to CF and CF to MSB.
- RCL − Used to rotate bits of byte/word towards the left, i.e. MSB to CF and CF to LSB.
String Instructions
String is a group of bytes/words and their memory is always allocated in a sequential order.
Following is the list of instructions under this group:
- REP − Used to repeat the given instruction till CX ≠ 0.
- REPE/REPZ − Used to repeat the given instruction until CX = 0 or zero flag ZF = 1.
- REPNE/REPNZ − Used to repeat the given instruction until CX = 0 or zero flag ZF = 1.
- MOVS/MOVSB/MOVSW − Used to move the byte/word from one string to another.
- COMS/COMPSB/COMPSW − Used to compare two string bytes/words.
- INS/INSB/INSW − Used as an input string/byte/word from the I/O port to the provided memory location.
- OUTS/OUTSB/OUTSW − Used as an output string/byte/word from the provided memory location to the I/O port.
- SCAS/SCASB/SCASW − Used to scan a string and compare its byte with a byte in AL or string word with a word in AX.
- LODS/LODSB/LODSW − Used to store the string byte into AL or string word into AX.
Program Execution Transfer Instructions (Branch and Loop Instructions)
These instructions are used to transfer/branch the instructions during an execution. It includes the following instructions −
Instructions to transfer the instruction during an execution without any condition:
- CALL − Used to call a procedure and save their return address to the stack.
- RET − Used to return from the procedure to the main program.
- JMP − Used to jump to the provided address to proceed to the next instruction.
- Instructions to transfer the instruction during an execution with some conditions −
- JA/JNBE − Used to jump if above/not below/equal instruction satisfies.
- JAE/JNB − Used to jump if above/not below instruction satisfies.
- JBE/JNA − Used to jump if below/equal/ not above instruction satisfies.
- JC − Used to jump if carry flag CF = 1
- JE/JZ − Used to jump if equal/zero flag ZF = 1
- JG/JNLE − Used to jump if greater/not less than/equal instruction satisfies.
- JGE/JNL − Used to jump if greater than/equal/not less than instruction satisfies.
- JL/JNGE − Used to jump if less than/not greater than/equal instruction satisfies.
- JLE/JNG − Used to jump if less than/equal/if not greater than instruction satisfies.
- JNC − Used to jump if no carry flag (CF = 0)
- JNE/JNZ − Used to jump if not equal/zero flag ZF = 0
- JNO − Used to jump if no overflow flag OF = 0
- JNP/JPO − Used to jump if not parity/parity odd PF = 0
- JNS − Used to jump if not sign SF = 0
- JO − Used to jump if overflow flag OF = 1
- JP/JPE − Used to jump if parity/parity even PF = 1
- JS − Used to jump if sign flag SF = 1
Processor Control Instructions
These instructions are used to control the processor action by setting/resetting the flag values.
Following are the instructions under this group:
- STC − Used to set carry flag CF to 1
- CLC − Used to clear/reset carry flag CF to 0
- CMC − Used to put complement at the state of carry flag CF.
- STD − Used to set the direction flag DF to 1
- CLD − Used to clear/reset the direction flag DF to 0
- STI − Used to set the interrupt enable flag to 1, i.e., enable INTR input.
- CLI − Used to clear the interrupt enable flag to 0, i.e., disable INTR input.
Iteration Control Instructions
These instructions are used to execute the given instructions for number of times. Following is the list of instructions under this group −
- LOOP − Used to loop a group of instructions until the condition satisfies, i.e., CX = 0
- LOOPE/LOOPZ − Used to loop a group of instructions till it satisfies ZF = 1 & CX = 0
- LOOPNE/LOOPNZ − Used to loop a group of instructions till it satisfies ZF = 0 & CX = 0
- JCXZ − Used to jump to the provided address if CX = 0
Interrupt Instructions
These instructions are used to call the interrupt during program execution.
- INT − Used to interrupt the program during execution and calling service specified.
- INTO − Used to interrupt the program during execution if OF = 1
- IRET − Used to return from interrupt service to the main program

0 Comments