Components of the Database System Environment
- There are five major components in the database system environment and their interrelationships are.
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Users
- Procedures
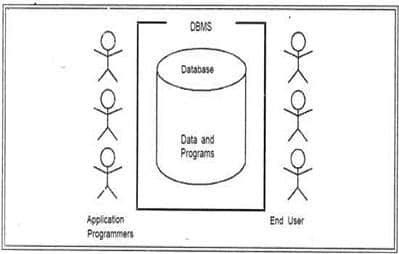
Hardware:
- The hardware is the actual computer system used for keeping and accessing the database.
- Conventional DBMS hardware consists of secondary storage devices, usually hard disks, on which the database physically resides.
- Databases run on a range of machines, from Microcomputers to large mainframes.
Software:
- The software is the actual DBMS.
- All requests from users for accessing to the database are handled by the DBMS.
- One general function provided by the DBMS is thus the shielding of database users from complex hardware-level detail.
- The DBMS allows the users to communicate with the database. In a sense, it is the mediator between the database and the users.
- The DBMS controls the access and helps to maintain the consistency of the data. Utilities are usually included as part of the DBMS. Some of the most common utilities are report writers and application development.
Data :
- It is the most important component of DBMS environment from the end users point of view.
- The database contains the operational data and the meta data, the ‘data about data‘(a set of data that describes and gives information about other data).
Users :
- There are a number of users who can access or retrieve data on demand using the applications and interfaces provided by the DBMS.
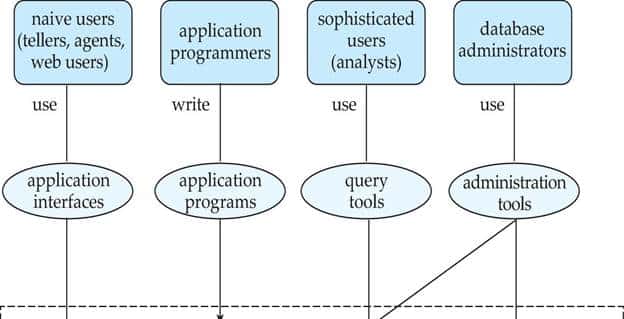
- The users of a database system can be classified in the following groups, depending on their degrees of expertise or the mode of their interactions with the DBMS. The users can be:
- Naive Users
- Online Users
- Application Programmers
- Sophisticated Users
- Data Base Administrator (DBA)
Users
Naive Users:
- Naive Users are those users who need not be aware of the presence of the database system or any other system supporting their usage.
- Naive users are end users of the database who work through a menu driven application program, where the type and range of response is always indicated to the user.
Online Users :
- Online users are those who may communicate with the database directly via an online terminal or indirectly via a user interface and application program.
- These users are aware of the presence of the database system and may have acquired a certain amount of expertise with in the limited interaction permitted with a database.
Sophisticated Users :
- Such users interact with the system without writing programs.
- Instead, they form their requests in database query language. Each query is submitted to a processor whose function is to breakdown DML statement into instructions that the storage manager understands.
Application Programmers :
- Professional programmers are those who are responsible for developing application programs or user interface.
- The application programs could be written using general purpose programming language or the commands available to manipulate a database.
Database Administrator:
- The database administrator (DBA) is the person or group in charge for implementing the database system within an organization.
- The DBA has all the system privileges allowed by the DBMS and can assign (grant) and remove (revoke) levels of access (privileges) to and from other users.
- DBA is also responsible for the evaluation, selection and implementation of DBMS package.
Components of the Database System Environment
Procedures:
- Procedures refer to the instructions and rules that govern the design and use of the database.
- The users of the system and the staff that manage the database require documented procedures on how to use or run the system.
Procedures:
These may consist of instructions on how to:
- Log on to the DBMS.
- Use a particular DBMS facility or application program.
- Start and stop the DBMS.
- Make backup copies of the database.
- Handle hardware or software failures.
- Change the structure of a table, reorganize the database across multiple disks, improve performance, or archive data to secondary storage.
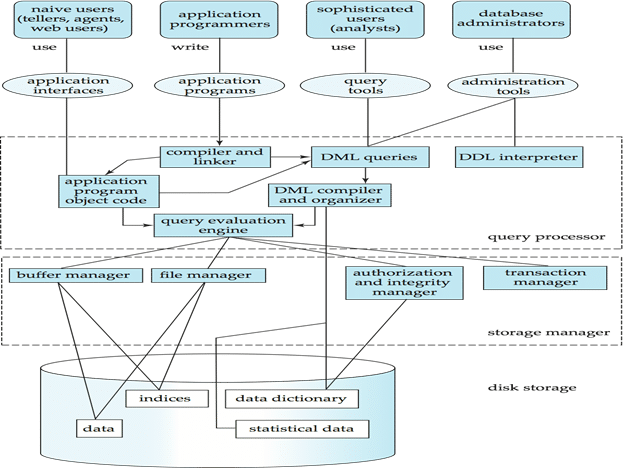
Database Architecture
Database design
- Front end design
- Back end design
Database Layer
- User Front end design
- Application program
- Query processor Back end design
- Storage manager

0 Comments